Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > Headache Pain Res > Volume 26(1); 2025 > Article
-
Original Article
Evidence-Based Recommendations on Pharmacologic Treatment for Migraine Prevention: A Clinical Practice Guideline from the Korean Headache Society -
Byung-Su Kim1
 , Pil-Wook Chung2
, Pil-Wook Chung2 , Jae Myun Chung3
, Jae Myun Chung3 , Kwang-Yeol Park4
, Kwang-Yeol Park4 , Heui-Soo Moon2
, Heui-Soo Moon2 , Hong-Kyun Park5
, Hong-Kyun Park5 , Dae-Woong Bae6
, Dae-Woong Bae6 , Jong-Geun Seo7
, Jong-Geun Seo7 , Jong-Hee Sohn8
, Jong-Hee Sohn8 , Tae-Jin Song9
, Tae-Jin Song9 , Seung-Han Lee10
, Seung-Han Lee10 , Kyungmi Oh11
, Kyungmi Oh11 , Mi Ji Lee12
, Mi Ji Lee12 , Myoung-Jin Cha13
, Myoung-Jin Cha13 , Yun-Ju Choi14
, Yun-Ju Choi14 , Miyoung Choi15
, Miyoung Choi15 , The Clinical Practice Guideline Committee of the Korean Headache Society
, The Clinical Practice Guideline Committee of the Korean Headache Society -
Headache and Pain Research 2025;26(1):5-20.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.62087/hpr.2024.0019
Published online: January 16, 2025
1Department of Neurology, Ewha Womans University Mokdong Hospital, Ewha Womans University College of Medicine, Seoul, Republic of Korea
2Department of Neurology, Kangbuk Samsung Hospital, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Republic of Korea
3Department of Neurology, H Plus Yangji Hospital, Seoul, Republic of Korea
4Department of Neurology, Chung-Ang University Hospital, Seoul, Republic of Korea
5Department of Neurology, Inje University Ilsan Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Goyang, Republic of Korea
6Department of Neurology, St. Vincent’s Hospital, The Catholic University of Korea, Suwon, Republic of Korea
7Department of Neurology, Kyungpook National University School of Medicine, Daegu, Republic of Korea
8Department of Neurology, Chuncheon Sacred Heart Hospital, Hallym University College of Medicine, Chuncheon, Republic of Korea
9Department of Neurology, Ewha Womans University Seoul Hospital, Ewha Womans University College of Medicine, Seoul, Republic of Korea
10Department of Neurology, Chonnam National University Medical School, Gwangju, Republic of Korea
11Department of Neurology, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Republic of Korea
12Department of Neurology, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Republic of Korea
13Department of Neurology, National Police Hospital, Seoul, Republic of Korea
14Dr. Choi’s Neurology Clinic, Jeonju, Republic of Korea
15Division Healthcare Research, National Evidence-based Healthcare Collaborating Agency, Seoul, Republic of Korea
- Correspondence: Pil-Wook Chung, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Neurology, Kangbuk Samsung Hospital, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, 29 Saemunan-ro, Jongno-gu, Seoul 03181, Republic of Korea Tel: +82-2-2001-2050, Fax: +82-2-2001-2049, E-mail: chungpw@hanmail.net
© 2025 The Korean Headache Society
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
- 12,682 Views
- 252 Download
- 11 Crossref
Abstract
-
Purpose
- The aim of this clinical practice guideline (CPG) from the Korean Headache Society is to provide evidence-based recommendations on the pharmacologic treatment for migraine prevention in adult migraine patients.
-
Methods
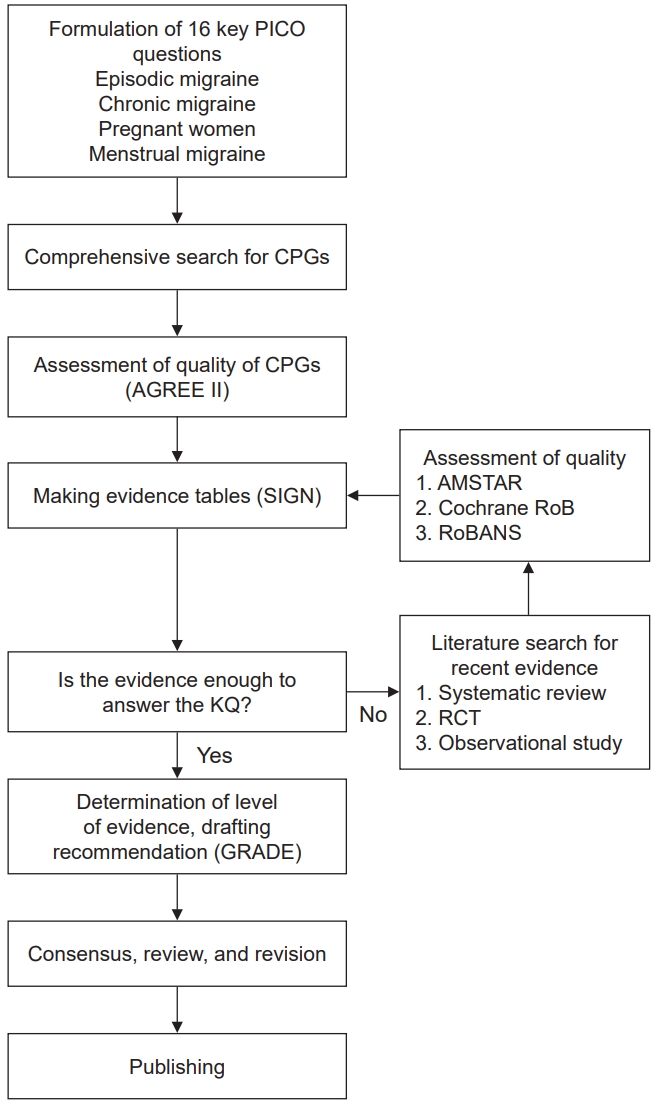
- The present CPG was developed based on the guideline adaptation methodology through a comprehensive systematic search for literature published between January 2012 and July 2020. The overall quality of the CPGs was assessed using the Korean version of the Appraisal of Guidelines for Research and Evaluation II tool. High-quality CPGs were adapted to make key recommendations in terms of strength (strong or weak) and direction (for or against).
-
Results
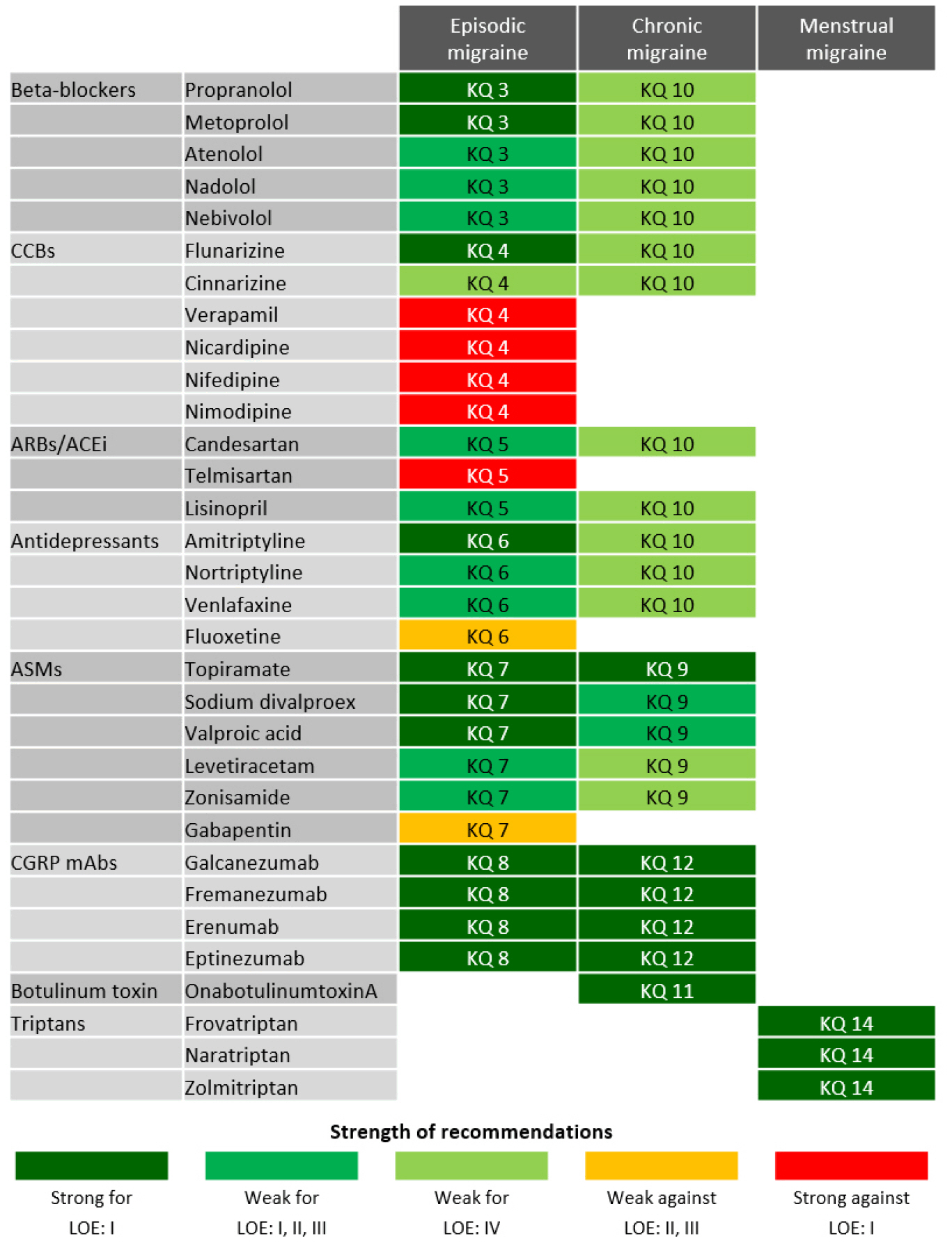
- The authors selected nine available high-quality guidelines throughout the process of assessment of quality. Regarding oral migraine preventive medications, propranolol, metoprolol, flunarizine, sodium divalproex, and valproic acid are recommended to adult patients with episodic migraines based on high-quality evidence (“strong for”). Topiramate can be recommended for either episodic or chronic migraine (“strong for”). For migraine prevention using calcitonin gene-related peptide monoclonal antibodies, galcanezumab, fremanezumab, erenumab, and eptinezumab are recommended for adult patients with either episodic or chronic migraine on the basis of high-quality evidence (“strong for”). OnabotulinumtoxinA is recommended for adult patients with chronic migraine based on high-quality evidence (“strong for”). Last, frovatriptan, naratriptan, and zolmitriptan are recommended for short-term prevention in women with menstrual migraine (“strong for”).
-
Conclusion
- In the present CPG, the authors provide specific, straightforward, and easy-to-implement evidence-based recommendations for pharmacologic migraine prevention. Nevertheless, these recommendations should be applied in real-world clinical practice based on optimal individualization.
INTRODUCTION
MATERIALS AND METHODS
RESULTS
1) Analysis of evidence
2) Recommendation
1) Analysis of evidence
2) Recommendation
1) Analysis of evidence
2) Recommendation
1) Analysis of evidence
2) Recommendation
1) Analysis of evidence
2) Recommendation
1) Analysis of evidence
2) Recommendation
1) Analysis of evidence
2) Recommendation
3) Additional consideration
1) Analysis of evidence
2) Recommendation
1) Analysis of evidence
2) Recommendation
3) Additional consideration
1) Analysis of evidence
2) Recommendation
1) Analysis of evidence
2) Recommendation
1) Analysis of evidence
2) Recommendation
1) Analysis of evidence
2) Recommendation
1) Analysis of evidence
2) Recommendation
AVAILABILITY OF DATA AND MATERIAL
Not applicable.
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS
Conceptualization: BSK, PWC, JMC, KYP, MC; Data curation: BSK, PWC, JMC, KYP, MC; Formal analysis: BSK, PWC, JMC, KYP, MC; Investigation: BSK, PWC, JMC, KYP, HSM, HKP, DWB, JGS, JHS, TJS, SHL, KO, MJL, MJC, YJC; Methodology: BSK, PWC, JMC, KYP, MC; Supervision: BSK, PWC, JMC, KYP, MC; Writing–original draft: BSK, PWC, JMC, KYP, HSM, HKP, DWB, JGS, JHS, TJS, SHL, KO, MJL, MJC, YJC; Writing–review & editing: BSK, PWC, JMC, KYP.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
FUNDING STATEMENT
Not applicable.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We thank external panels for reviewing the current CPG and giving helpful advice.
| Clinical practice guideline | Domain 1: Scope and purpose | Domain 2: Stakeholder involvement | Domain 3: Rigour of development | Domain 4: Clarity of presentation | Domain 5: Applicability | Domain 6: Editorial independence | Overall assessment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2012 AHS/AAN8 | 94.4 | 77.8 | 88.5 | 91.7 | 79.2 | 100.0 | 87.5 |
| 2012 Canadian Headache Society9 | 100.0 | 94.4 | 96.9 | 100.0 | 91.7 | 100.0 | 95.8 |
| 2012 Croatian Medical Association10 | 52.8 | 47.2 | 32.3* | 69.4 | 14.6 | 0.0 | 66.7 |
| 2012 Danish Headache Society11 | 91.7 | 66.7 | 24.0* | 75.0 | 20.8 | 100.0 | 58.3 |
| 2012 SFEMC12 | 77.8 | 77.8 | 76.0 | 91.7 | 43.8 | 87.5 | 83.3 |
| 2012 SISC13 | 63.9 | 55.6 | 60.4 | 88.9 | 31.3 | 66.7 | 75.0 |
| 2013 ICSI14 | 94.4 | 86.1 | 90.6 | 86.1 | 64.6 | 95.8 | 95.8 |
| 2015 NICE15 | 50.0 | 50.0 | 31.3* | 72.2 | 16.7 | 0.0 | 41.7 |
| 2016 AAN16 | 80.6 | 44.4 | 41.7* | 50.0 | 0.0 | 100.0 | 70.8 |
| 2019 AHS17 | 63.9 | 63.9 | 46.9* | 69.4 | 45.8 | 45.8 | 54.2 |
| 2017 RSSHA18 | 61.1 | 52.8 | 34.4* | 47.2 | 50.0 | 58.3 | 33.3 |
| 2020 EAN19 | 97.2 | 58.3 | 74.0 | 97.2 | 45.8 | 83.3 | 66.7 |
| 2019 EHF20 | 97.2 | 61.1 | 81.3 | 94.4 | 50.0 | 66.7 | 75.0 |
| 2019 Spanish Society of Neurology21 | 16.7 | 22.2 | 7.3* | 13.9 | 16.7 | 66.7 | 41.7 |
| 2015 Alberta, Canada22 | 66.7 | 44.4 | 51.0* | 75.0 | 25.0 | 87.5 | 37.5 |
| 2018 EHF23 | 77.8 | 52.8 | 62.5 | 72.2 | 37.5 | 54.2 | 79.2 |
| 2018 EMA/EHF24 | 61.1 | 61.1 | 40.6* | 52.8 | 54.2 | 79.2 | 62.5 |
| 2013 Latin American and Brazilian Headache Societies25 | 66.7 | 44.4 | 35.4* | 61.1 | 16.7 | 50.0 | 58.3 |
| 2018 SIGN26 | 100.0 | 77.8 | 93.8 | 100.0 | 58.3 | 75.0 | 83.3 |
Values are average scores independently rated rated by two development working members using the AGREE II framework.
AGREE, Appraisal of Guidelines for Research and Evaluation; AHS, American Headache Society; AAN, American Academy of Neurology; SFEMC, French Society for the Study of Migraine Headache; SISC, Italian Society for the Study of Headaches; ICSI, Institute for Clinical Systems Improvement; NICE, National Institute for Health and Care Excellence; RSSHA, Russian Society for the Study of Headache; EAN, European Academy of Neurology; EHF, European Headache Federation; EMA, European Medicines Agency; SIGN, Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network.
*Guidelines that scored less than 60% in the domain 3. Rigour of development were excluded.
- 1. Ashina M, Terwindt GM, Al-Karagholi MA, et al. Migraine: disease characterisation, biomarkers, and precision medicine. Lancet 2021;397:1496-1504.ArticlePubMed
- 2. Ashina M, Katsarava Z, Do TP, et al. Migraine: epidemiology and systems of care. Lancet 2021;397:1485-1495.ArticlePubMed
- 3. Kim BK, Chu MK, Lee TG, Kim JM, Chung CS, Lee KS. Prevalence and impact of migraine and tension-type headache in Korea. J Clin Neurol 2012;8:204-211.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 4. Steiner TJ, Stovner LJ, Jensen R, Uluduz D, Katsarava Z; Lifting The Burden: the Global Campaign against Headache. Migraine remains second among the world’s causes of disability, and first among young women: findings from GBD2019. J Headache Pain 2020;21:137.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 5. Headache Classification Committee of the International Headache Society (IHS). The International Classification of Headache Disorders, 3rd edition. Cephalalgia 2018;38:1-211.ArticlePDF
- 6. Guyatt GH, Oxman AD, Vist GE, et al. GRADE: an emerging consensus on rating quality of evidence and strength of recommendations. BMJ 2008;336:924-926.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 7. Schardt C, Adams MB, Owens T, Keitz S, Fontelo P. Utilization of the PICO framework to improve searching PubMed for clinical questions. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak 2007;7:16.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 8. Silberstein SD, Holland S, Freitag F, et al. Evidence-based guideline update: pharmacologic treatment for episodic migraine prevention in adults: report of the Quality Standards Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology and the American Headache Society. Neurology 2012;78:1337-1345.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 9. Pringsheim T, Davenport W, Mackie G, et al. Canadian Headache Society guideline for migraine prophylaxis. Can J Neurol Sci 2012;392:S1-S59.PubMed
- 10. Vuković Cvetković V, Kes VB, Serić V, et al. Report of the Croatian Society for Neurovascular Disorders, Croatian Medical Association. Evidence based guidelines for treatment of primary headaches: 2012 update. Acta Clin Croat 2012;51:323-378.PubMed
- 11. Bendtsen L, Birk S, Kasch H, et al. Reference programme: diagnosis and treatment of headache disorders and facial pain. Danish Headache Society, 2nd Edition, 2012. J Headache Pain 2012;13 Suppl 1:S1-S29.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 12. Lanteri-Minet M, Valade D, Geraud G, Lucas C, Donnet A. Revised French guidelines for the diagnosis and management of migraine in adults and children. J Headache Pain 2014;15:2.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 13. Sarchielli P, Granella F, Prudenzano MP, et al. Italian guidelines for primary headaches: 2012 revised version. J Headache Pain 2012;13 Suppl 2:S31-S70.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 14. Beithon J, Gallenberg M, Johnson K, et al. Diagnosis and treatment of headache [Interrnet]. Institute for Clinical Systems Improvement; 2013 [updated 2013 Jan; cited 2024 Jun 22]. Available from: https://www.icsi.org/guidelines__more/catalog_guidelines_and_more/catalog_guidelines/catalog_neurological_guidelines/headache/
- 15. National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE). Headaches in over 12s: diagnosis and management [Interrnet]. NICE; 2012 [updated 2015; cited 2024 Jun 22]. Available from: https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/CG150
- 16. Simpson DM, Hallett M, Ashman EJ, et al. Practice guideline update summary: Botulinum neurotoxin for the treatment of blepharospasm, cervical dystonia, adult spasticity, and headache: report of the Guideline Development Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology. Neurology 2016;86:1818-1826.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 17. American Headache Society. The American Headache Society position statement on integrating new migraine treatments into clinical practice. Headache 2019;59:1-18.ArticlePDF
- 18. Osipova VV, Filatova EG, Artemenko AR, et al. [Diagnosis and treatment of migraine: recommendations of the Russian experts]. Zh Nevrol Psikhiatr Im S S Korsakova 2017;117:28-42. Russian.Article
- 19. Diener HC, Antonaci F, Braschinsky M, et al. European Academy of Neurology guideline on the management of medication-overuse headache. Eur J Neurol 2020;27:1102-1116.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 20. Sacco S, Bendtsen L, Ashina M, et al. European headache federation guideline on the use of monoclonal antibodies acting on the calcitonin gene related peptide or its receptor for migraine prevention. J Headache Pain 2019;20:6.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 21. Gago-Veiga AB, Santos-Lasaosa S, Cuadrado ML, et al. Evidence and experience with onabotulinumtoxinA in chronic migraine: recommendations for daily clinical practice. Neurologia (Engl Ed) 2019;34:408-417.ArticlePubMed
- 22. Becker WJ, Findlay T, Moga C, Scott NA, Harstall C, Taenzer P. Guideline for primary care management of headache in adults. Can Fam Physician 2015;61:670-679.PubMedPMC
- 23. Bendtsen L, Sacco S, Ashina M, et al. Guideline on the use of onabotulinumtoxinA in chronic migraine: a consensus statement from the European Headache Federation. J Headache Pain 2018;19:91.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 24. Vatzaki E, Straus S, Dogne JM, Garcia Burgos J, Girard T, Martelletti P. Latest clinical recommendations on valproate use for migraine prophylaxis in women of childbearing age: overview from European Medicines Agency and European Headache Federation. J Headache Pain 2018;19:68.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 25. Giacomozzi AR, Vindas AP, Silva AA Jr, et al. Latin American consensus on guidelines for chronic migraine treatment. Arq Neuropsiquiatr 2013;71:478-486.ArticlePubMed
- 26. Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network (SIGN). Pharmacological management of migraine. SIGN; 2018 [cited 2024 Jun 22]. Available from: https://www.sign.ac.uk/our-guidelines/pharmacological-management-of-migraine/
- 27. Brouwers MC, Kerkvliet K, Spithoff K; AGREE Next Steps Consortium. The AGREE Reporting Checklist: a tool to improve reporting of clinical practice guidelines. BMJ 2016;352:i1152.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 28. Hoffmann-Eßer W, Siering U, Neugebauer EA, Brockhaus AC, Lampert U, Eikermann M. Guideline appraisal with AGREE II: systematic review of the current evidence on how users handle the 2 overall assessments. PLoS One 2017;12:e0174831.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 29. Ko SB, Park HK, Kim BM, et al. 2019 Update of the Korean Clinical Practice Guidelines of Stroke for endovascular recanalization therapy in patients with acute ischemic stroke. J Stroke 2019;21:231-240.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 30. Guyatt GH, Oxman AD, Kunz R, et al. Going from evidence to recommendations. BMJ 2008;336:1049-1051.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 31. Jackson JL, Kuriyama A, Kuwatsuka Y, et al. Beta-blockers for the prevention of headache in adults, a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One 2019;14:e0212785.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 32. Jackson JL, Cogbill E, Santana-Davila R, et al. A comparative effectiveness meta-analysis of drugs for the prophylaxis of migraine headache. PLoS One 2015;10:e0130733.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 33. Stubberud A, Flaaen NM, McCrory DC, Pedersen SA, Linde M. Flunarizine as prophylaxis for episodic migraine: a systematic review with meta-analysis. Pain 2019;160:762-772.ArticlePubMed
- 34. Watkins AK, Gee ME, Brown JN. Efficacy and safety of levetiracetam for migraine prophylaxis: a systematic review. J Clin Pharm Ther 2018;43:467-475.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 35. Tsaousi G, Pourzitaki C, Siafis S, et al. Levetiracetam as preventive treatment in adults with migraine: an up-to-date systematic review and quantitative meta-analysis. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 2020;76:161-174.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 36. Mohammadianinejad SE, Abbasi V, Sajedi SA, et al. Zonisamide versus topiramate in migraine prophylaxis: a double-blind randomized clinical trial. Clin Neuropharmacol 2011;34:174-177.ArticlePubMed
- 37. Assarzadegan F, Tabesh H, Hosseini-Zijoud SM, et al. Comparing zonisamide with sodium valproate in the management of migraine headaches: double-blind randomized clinical trial of efficacy and safety. Iran Red Crescent Med J 2016;18:e23768.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 38. Ashina M, Saper J, Cady R, et al. Eptinezumab in episodic migraine: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study (PROMISE-1). Cephalalgia 2020;40:241-254.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 39. Lattanzi S, Brigo F, Trinka E, et al. Erenumab for preventive treatment of migraine: a systematic review and meta-analysis of efficacy and safety. Drugs 2019;79:417-431.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 40. Alasad YW, Asha MZ. Monoclonal antibodies as a preventive therapy for migraine: a meta-analysis. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 2020;195:105900.ArticlePubMed
- 41. Deng H, Li GG, Nie H, et al. Efficacy and safety of calcitonin-gene-related peptide binding monoclonal antibodies for the preventive treatment of episodic migraine - an updated systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Neurol 2020;20:57.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 42. Yang Y, Wang Z, Gao B, et al. Different doses of galcanezumab versus placebo in patients with migraine and cluster headache: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J Headache Pain 2020;21:14.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 43. Yan Z, Xue T, Chen S, et al. Different dosage regimens of eptinezumab for the treatment of migraine: a meta-analysis from randomized controlled trials. J Headache Pain 2021;22:10.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 44. Han L, Liu Y, Xiong H, Hong P. CGRP monoclonal antibody for preventive treatment of chronic migraine: an update of meta-analysis. Brain Behav 2019;9:e01215.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 45. Lipton RB, Goadsby PJ, Smith J, et al. Efficacy and safety of eptinezumab in patients with chronic migraine: PROMISE-2. Neurology 2020;94:e1365-e1377.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 46. MacGregor EA. Migraine in pregnancy and lactation. Neurol Sci 2014;35 Suppl 1:61-64.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 47. Negro A, Delaruelle Z, Ivanova TA, et al. Headache and pregnancy: a systematic review. J Headache Pain 2017;18:106.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 48. Hu Y, Guan X, Fan L, Jin L. Triptans in prevention of menstrual migraine: a systematic review with meta-analysis. J Headache Pain 2013;14:7.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 49. Nierenburg Hdel C, Ailani J, Malloy M, Siavoshi S, Hu NN, Yusuf N. Systematic review of preventive and acute treatment of menstrual migraine. Headache 2015;55:1052-1071.ArticlePubMed
- 50. Seo JG. Menstrual migraine: a review of current research and clinical challenges. Headache Pain Res 2024;25:16-23.ArticlePDF
REFERENCES
Figure & Data
References
Citations

- One-Year Compliance After Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide Monoclonal Antibody Therapy for Migraine Patients in a Real-World Setting: A Multicenter Cross-Sectional Study
Mi-kyoung Kang, Jong-Hee Sohn, Myoung-Jin Cha, Yoo Hwan Kim, Yooha Hong, Hee-Jin Im, Soo-Jin Cho
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2025; 14(3): 734. CrossRef - Beyond the Pain: Rethinking Migraine Care with the RELIEF PLAN Approach
Sanghyo Ryu
Headache and Pain Research.2025; 26(1): 1. CrossRef - Concurrent Extracerebral Vasoconstriction in Patients with Reversible Cerebral Vasoconstriction Syndrome: A Cross-Sectional Study
Byung-Su Kim, Sumin Kim, Eunhee Kim, Ick-Mo Chung, Sodam Jung, Yoonkyung Chang, Dong Woo Shin, Tae-Jin Song
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2025; 14(13): 4402. CrossRef - Validity of Migraine Diagnoses in Korean National Health Insurance Claims Data
Yoonkyung Chang, Soyoun Choi, Byung-Su Kim, Tae-Jin Song
Headache and Pain Research.2025; 26(2): 154. CrossRef - Tension-Type Headache and Primary Stabbing Headache: Primary Headaches Beyond Migraine
Mi-Kyoung Kang
Headache and Pain Research.2025; 26(2): 89. CrossRef - Injection-Based Therapies for Migraine in Older Adults: A Narrative Review of OnabotulinumtoxinA, Greater Occipital Nerve Block, and Anti Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide Monoclonal Antibodies
Mi-Kyoung Kang, Soohyun Cho, Byung-Kun Kim, Heui-Soo Moon, Mi Ji Lee, Soo-Kyoung Kim, Hong-Kyun Park, Min-Kyung Chu, Woo-Seok Ha, Byung-Su Kim, Soo-Jin Cho
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Use of Antiseizure Medications in Neurological Disorders Beyond Epilepsy
Kyung Min Kim, Byung-Su Kim, Hee-Jin Kim, Seung Woo Kim, Kyoungwon Baik, Jin Myoung Seok, Jun-Sang Sunwoo, In-Uk Song, Ho Geol Woo, Eek-Sung Lee, Jin-Man Jung, Kyomin Choi, Yun Ho Choi, Kwang Ik Yang
Journal of the Korean Neurological Association.2025; 43(4): 245. CrossRef - A Practical Approach to Headache in Moyamoya Disease
Mi-Yeon Eun, Jin-Man Jung, Jay Chol Choi
Headache and Pain Research.2025; 26(3): 173. CrossRef - Evolution of Migraine Treatment: Recent Drugs and Clinical Trial Trends
Yoon-Kyung Chang, Tae-Jin Song
NeuroTrials.2025; 1(1): 1. CrossRef - Clinical Effectiveness and Cost-Effectiveness of Collaborative Treatment With Korean and Western Medicine for Primary Headache Disorders: Protocol for a Multicenter Prospective Observational Study
Jaeseung Kim, Jihwan Yun, Linae Kim, Shiva Raj Acharya, Changyon Han, NamKwen Kim
JMIR Research Protocols.2025; 14: e82819. CrossRef - Clinical Practice Guideline Recommendations for Post-Acute Sequelae of COVID-19
Jun-Won Seo, Yu Bin Seo, Seong Eun Kim, Yoonjung Kim, Eun Jung Kim, Tark Kim, Taehwa Kim, So Hee Lee, Eunjung Lee, Jacob Lee, Yeong-Hoon Jeong, Yeong Hee Jung, Yu Jung Choi, Joon Young Song
Infection & Chemotherapy.2025; 57(4): 478. CrossRef
 PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link-
 Cite this Article
Cite this Article
- Cite this Article
-
- Close
- Download Citation
- Close
- Figure

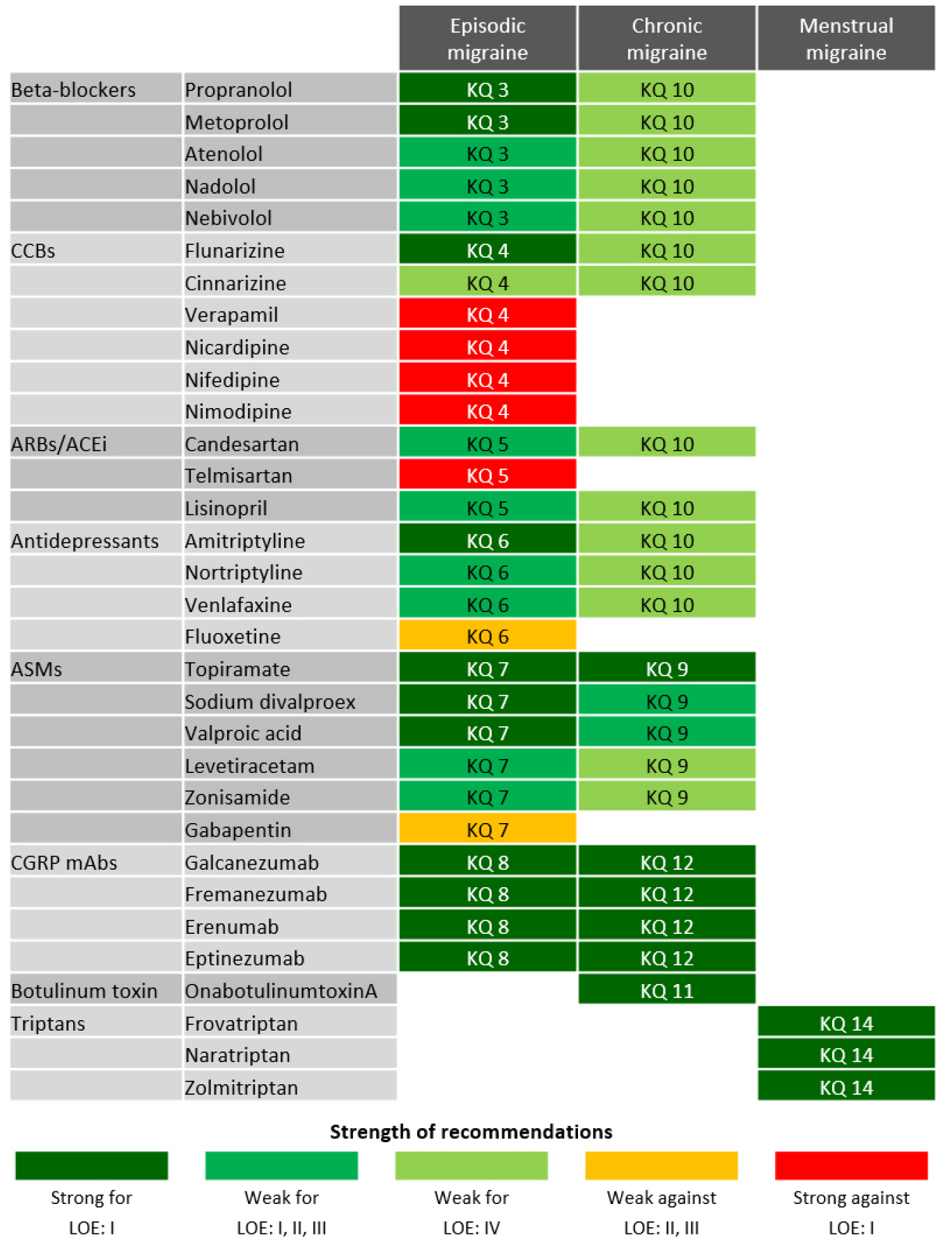
Figure 1.
Figure 2.
| Clinical practice guideline | Domain 1: Scope and purpose | Domain 2: Stakeholder involvement | Domain 3: Rigour of development | Domain 4: Clarity of presentation | Domain 5: Applicability | Domain 6: Editorial independence | Overall assessment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2012 AHS/AAN8 | 94.4 | 77.8 | 88.5 | 91.7 | 79.2 | 100.0 | 87.5 |
| 2012 Canadian Headache Society9 | 100.0 | 94.4 | 96.9 | 100.0 | 91.7 | 100.0 | 95.8 |
| 2012 Croatian Medical Association10 | 52.8 | 47.2 | 32.3 |
69.4 | 14.6 | 0.0 | 66.7 |
| 2012 Danish Headache Society11 | 91.7 | 66.7 | 24.0 |
75.0 | 20.8 | 100.0 | 58.3 |
| 2012 SFEMC12 | 77.8 | 77.8 | 76.0 | 91.7 | 43.8 | 87.5 | 83.3 |
| 2012 SISC13 | 63.9 | 55.6 | 60.4 | 88.9 | 31.3 | 66.7 | 75.0 |
| 2013 ICSI14 | 94.4 | 86.1 | 90.6 | 86.1 | 64.6 | 95.8 | 95.8 |
| 2015 NICE15 | 50.0 | 50.0 | 31.3 |
72.2 | 16.7 | 0.0 | 41.7 |
| 2016 AAN16 | 80.6 | 44.4 | 41.7 |
50.0 | 0.0 | 100.0 | 70.8 |
| 2019 AHS17 | 63.9 | 63.9 | 46.9 |
69.4 | 45.8 | 45.8 | 54.2 |
| 2017 RSSHA18 | 61.1 | 52.8 | 34.4 |
47.2 | 50.0 | 58.3 | 33.3 |
| 2020 EAN19 | 97.2 | 58.3 | 74.0 | 97.2 | 45.8 | 83.3 | 66.7 |
| 2019 EHF20 | 97.2 | 61.1 | 81.3 | 94.4 | 50.0 | 66.7 | 75.0 |
| 2019 Spanish Society of Neurology21 | 16.7 | 22.2 | 7.3 |
13.9 | 16.7 | 66.7 | 41.7 |
| 2015 Alberta, Canada22 | 66.7 | 44.4 | 51.0 |
75.0 | 25.0 | 87.5 | 37.5 |
| 2018 EHF23 | 77.8 | 52.8 | 62.5 | 72.2 | 37.5 | 54.2 | 79.2 |
| 2018 EMA/EHF24 | 61.1 | 61.1 | 40.6 |
52.8 | 54.2 | 79.2 | 62.5 |
| 2013 Latin American and Brazilian Headache Societies25 | 66.7 | 44.4 | 35.4 |
61.1 | 16.7 | 50.0 | 58.3 |
| 2018 SIGN26 | 100.0 | 77.8 | 93.8 | 100.0 | 58.3 | 75.0 | 83.3 |
| Medication | Range of daily dose or single injection dose (mg) | Adverse events |
|---|---|---|
| Beta-blockers | ||
| Propranolol | 20–160 | Fatigue, dizziness, depression, and vivid dreams |
| Metoprolol | 50–200 | Fatigue, dizziness, depression, and vivid dreams |
| Atenolol | 50–200 | Fatigue, dizziness, depression, vivid dreams, dyspnea, bradycardia, palpitation, and vomiting |
| Nadolol | 40–160 | Fatigue, dizziness, depression, vivid dreams, dyspnea, bradycardia, palpitation, and vomiting |
| Nebivolol | 2.5–5.0 | Headache, dizziness, dysesthesia, nightmare, gastrointestinal disorder, dyspnea, itching, and edema |
| Calcium channel-blocker | ||
| Flunarizine | 5–10 | Weight gain, somnolence, dry mouth, dizziness, hypotension, and depression |
| Cinnarizine | 25–50 | Weight gain, somnolence, dry mouth, dizziness, hypotension, and depression |
| Verapamil | 120–480 | Palpitation, edema, arrythmia, and rash |
| Nicardipine | 40–80 | Constipation, facial flushing, helplessness, headache, myalgia, tremor, and dizziness |
| Nifedipine | 15–60 | Constipation, facial flushing, helplessness, headache, myalgia, tremor, and dizziness |
| Nimodipine | 90 | Gastrointestinal disorder, headache, dizziness, somnolence, and tremor |
| Angiotensin receptor blockers and angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor | ||
| Candesartan | 4–16 | Hypotension and aggravation of congestive heart failure |
| Telmisartan | 40–80 | Hyperkalemia, dizziness, hypotension, rash, and myalgia |
| Lisinopril | 10–20 | Dizziness, headache, cough, fatigue, muscle cramps, diarrhea, and hypotension |
| Antidepressants | ||
| Amitriptyline | 2.5–50.0 | Weight gain, dry mouth, somnolence, fatigue, helplessness, dizziness, blurred vision, and constipation |
| Nortriptyline | 25–150 | Weight gain, dry mouth, somnolence, fatigue, helplessness, dizziness, blurred vision, and constipation |
| Venlafaxine | 37.5–150.0 | Somnolence, insomnia, dizziness, headache, vomiting, dry mouth, anxiety, and sexual dysfunction |
| Fluoxetine | 10–80 | Fatigue, vomiting, diarrhea, insomnia, loss of appetite, impotence, tremor, anxiety, and restlessness |
| Antiseizure medications | ||
| Topiramate | 12.5–150.0 | Paresthesia, fatigue, anorexia, diarrhea, weight loss, and difficulty with memory |
| Sodium divalproex | 250–1,500 | Nausea, vomiting, weight gain, tremor, hair loss, somnolence, and dizziness |
| Valproic acid | 600–2,000 | Nausea, vomiting, weight gain, tremor, hair loss, somnolence, and dizziness |
| Levetiracetam | 500–2,000 | Fatigue, helplessness, somnolence, myalgia, dizziness, diplopia, rash, and cough |
| Zonisamide | 100–600 | Weight loss, diplopia, visual disturbance, somnolence, ataxia, and abnormal thinking |
| Gabapentin | 300–1,800 | Peripheral edema, dizziness, somnolence, ataxia, and weight gain |
| Calcitonin gene-related peptide monoclonal antibody | ||
| Galcanezumab | 120 or 240 mg SC (monthly) | Injection site pain, injection site reaction, injection site erythema/pruritis, upper respiratory tract infection, and constipation |
| Fremanezumab | 225 mg SC (monthly) | Injection site pain, injection site reaction, injection site erythema/pruritis, upper respiratory tract infection, and constipation |
| 675 mg SC (quarterly) | ||
| Erenumab | 70 or 140 mg SC (monthly) | Injection site pain, injection site reaction, injection site erythema/pruritis, upper respiratory tract infection, and constipation |
| Eptinezumab | 100 or 300 mg IV (quarterly) | Hypersensitivity, infusion site extravasation, upper respiratory tract infection, and constipation |
| Botulinum toxin | ||
| OnabotulinumtoxinA | 155–195 units IM (12-wk interval) | Neck pain, muscular weakness, myalgia, injection site pain, and ptosis |
| Triptans | ||
| Frovatriptan | 2.5–5.0 | Triptan sensation, dizziness, somnolence, fatigue, lethargy, headache, and vomiting |
| Naratriptan | 1–2.0 | Triptan sensation, dizziness, somnolence, fatigue, lethargy, headache, and vomiting |
| Zolmitriptan | 2.5–7.5 | Triptan sensation, dizziness, somnolence, fatigue, lethargy, headache, and vomiting |
Values are average scores independently rated rated by two development working members using the AGREE II framework. AGREE, Appraisal of Guidelines for Research and Evaluation; AHS, American Headache Society; AAN, American Academy of Neurology; SFEMC, French Society for the Study of Migraine Headache; SISC, Italian Society for the Study of Headaches; ICSI, Institute for Clinical Systems Improvement; NICE, National Institute for Health and Care Excellence; RSSHA, Russian Society for the Study of Headache; EAN, European Academy of Neurology; EHF, European Headache Federation; EMA, European Medicines Agency; SIGN, Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network. Guidelines that scored less than 60% in the domain 3. Rigour of development were excluded.
SC, subcutaneous; IV, intravenous; IM, intramuscular.
Table 1.
Table 2.
TOP
 KHS
KHS





