Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > Headache Pain Res > Volume 26(2); 2025 > Article
-
Review Article
Efficacy and Safety of Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation in Postherpetic Neuralgia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis -
Abdallah Abbas1
 , Basant Lashin2
, Basant Lashin2 , Mohamed Abouzid3,4
, Mohamed Abouzid3,4 , Hadir Mustafa Mohamed5
, Hadir Mustafa Mohamed5 , Mohamed El-Moslemani1
, Mohamed El-Moslemani1 , Mohamed A. Zanaty6
, Mohamed A. Zanaty6 , Haneen Sabet6
, Haneen Sabet6 , Dina Essam Abo-elnour7
, Dina Essam Abo-elnour7 , Ahmed Ibrahim Ghonimy Shedid8, Mohamed Salah Mohamed Syed9, Amna Hussein10
, Ahmed Ibrahim Ghonimy Shedid8, Mohamed Salah Mohamed Syed9, Amna Hussein10 , Hoda Awad11
, Hoda Awad11 , Ahmed M. Raslan12
, Ahmed M. Raslan12
-
Headache and Pain Research 2025;26(2):91-105.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.62087/hpr.2024.0032
Published online: April 16, 2025
1Faculty of Medicine, Al-Azhar University, Damietta, Egypt
2Benha Faculty of Medicine, Benha, Egypt
3Department of Physical Pharmacy and Pharmacokinetics, Faculty of Pharmacy, Poznan University of Medical Sciences, Poznan, Poland
4Doctoral School, Poznan University of Medical Sciences, Poznan, Poland
5Faculty of Medicine, Alexandria University, Alexandria, Egypt
6Faculty of Medicine, South Valley University, Qena, Egypt
7Faculty of Medicine, Zagazig University, Zagazig, Egypt
8Sharm Elsheikh International Hospital, South Sinai, Egypt
9Faculty of Medicine, Ain Shams University, Cairo, Egypt
10Department of Neurosurgery, University of Arizona College of Medicine, Phoenix, AZ, USA
11Faculty of Medicine, Cairo University, Cairo, Egypt
12Department of Neurological Surgery, Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, OR, USA
- Correspondence: Abdallah Abbas, MD Faculty of Medicine, Al-Azhar University, 2nd district, New Damietta 34517, Damietta, Egypt Tel: +20-1070019529, E-mail: abdallah.abdelmoneam.abbas@gmail.com
© 2025 The Korean Headache Society
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
- 12,184 Views
- 80 Download
Abstract
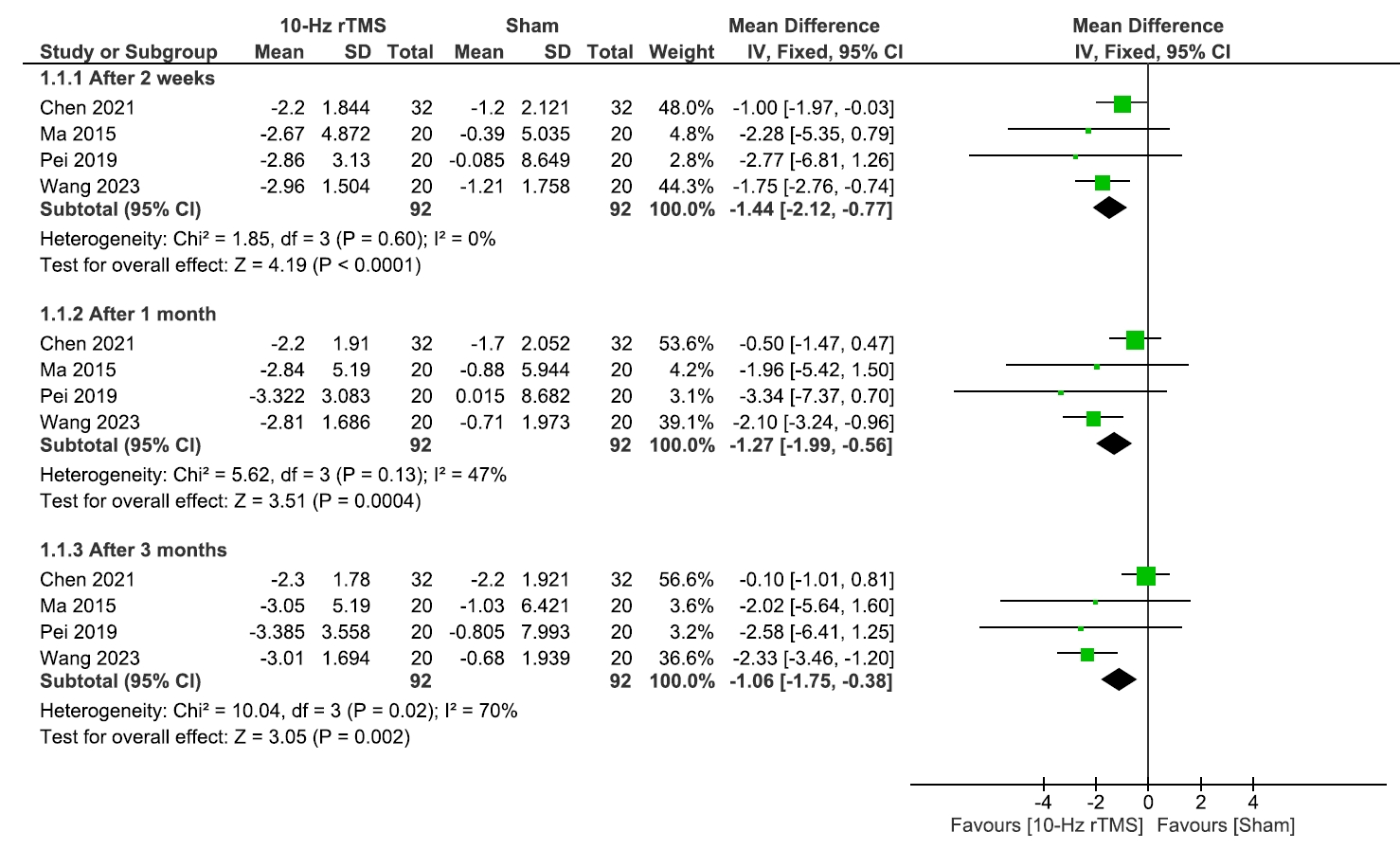
- This study evaluated the efficacy and safety of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS) for pain management in postherpetic neuralgia (PHN). A comprehensive literature search was conducted through May 2024 in Scopus, PubMed, Web of Science, and Cochrane Library. Eligible studies included clinical trials, observational, and case-control studies. Two reviewers independently screened studies and extracted data. Risk of bias was assessed using RoB 2 for randomized controlled trials and the Newcastle-Ottawa Scale for observational studies. Meta-analysis was performed using Review Manager v.5.3, with heterogeneity evaluated by chi-square and I² tests. Five studies (245 patients) were included, with rTMS sessions ranging from 10 to 28. Meta-analysis showed significant pain reduction with rTMS compared to sham treatment. At 2 weeks post-treatment, the mean pain score difference (visual analogue scale) was –1.44 (95% confidence interval: –2.12 to –0.77; p<0.0001), with sustained relief at 1 and 3 months. However, no significant differences were found in the patient’s global impression of change scale, sleep quality, quality of life (QoL), medication regulation, or adverse events. rTMS exerted a consistent pain relief effect of rTMS, but its impact on broader aspects of patient well-being was less clear. rTMS provides sustained pain relief in PHN for up to 3 months, but its impact on QoL and secondary outcomes remains unclear, warranting further investigation.
INTRODUCTION
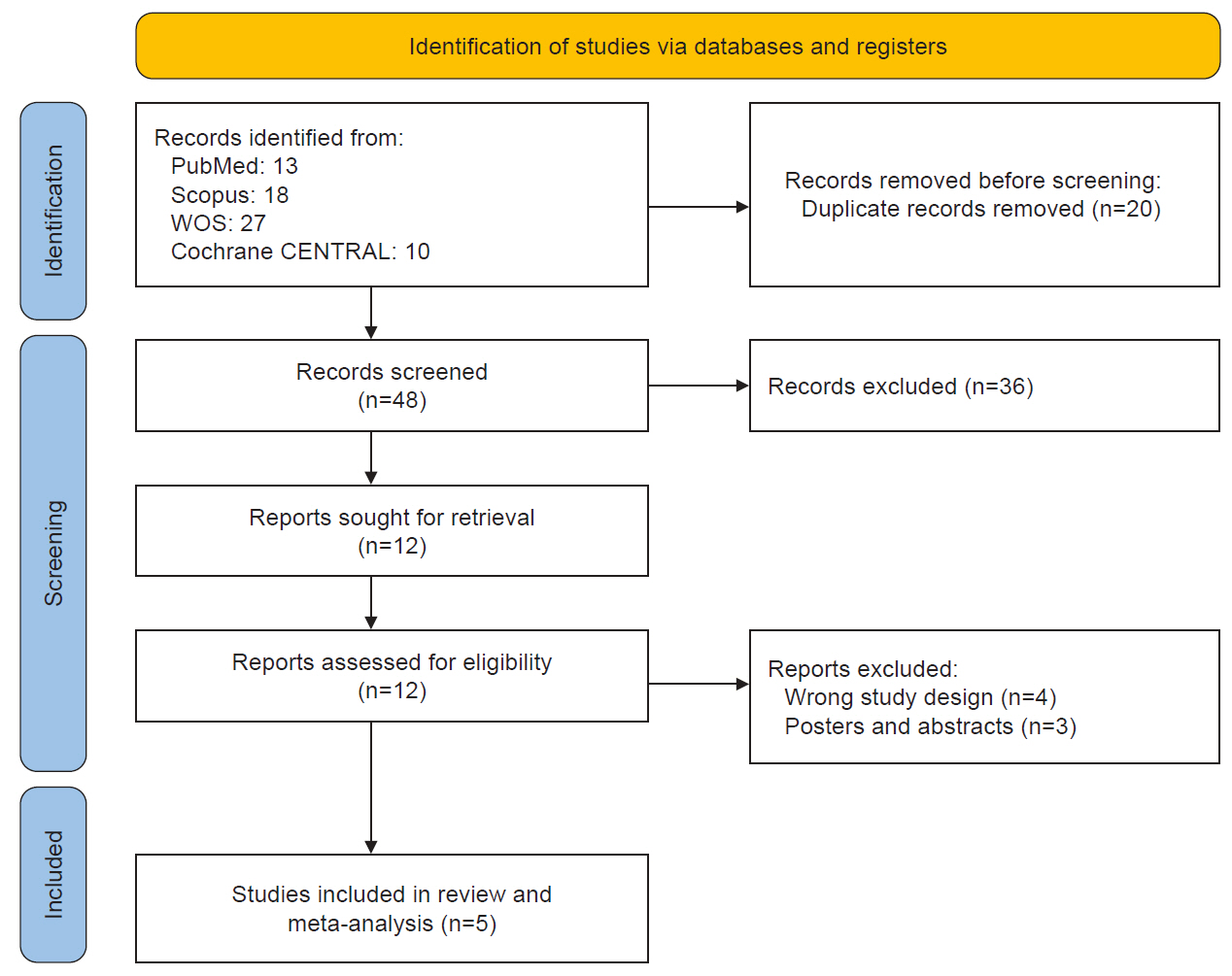
METHODS
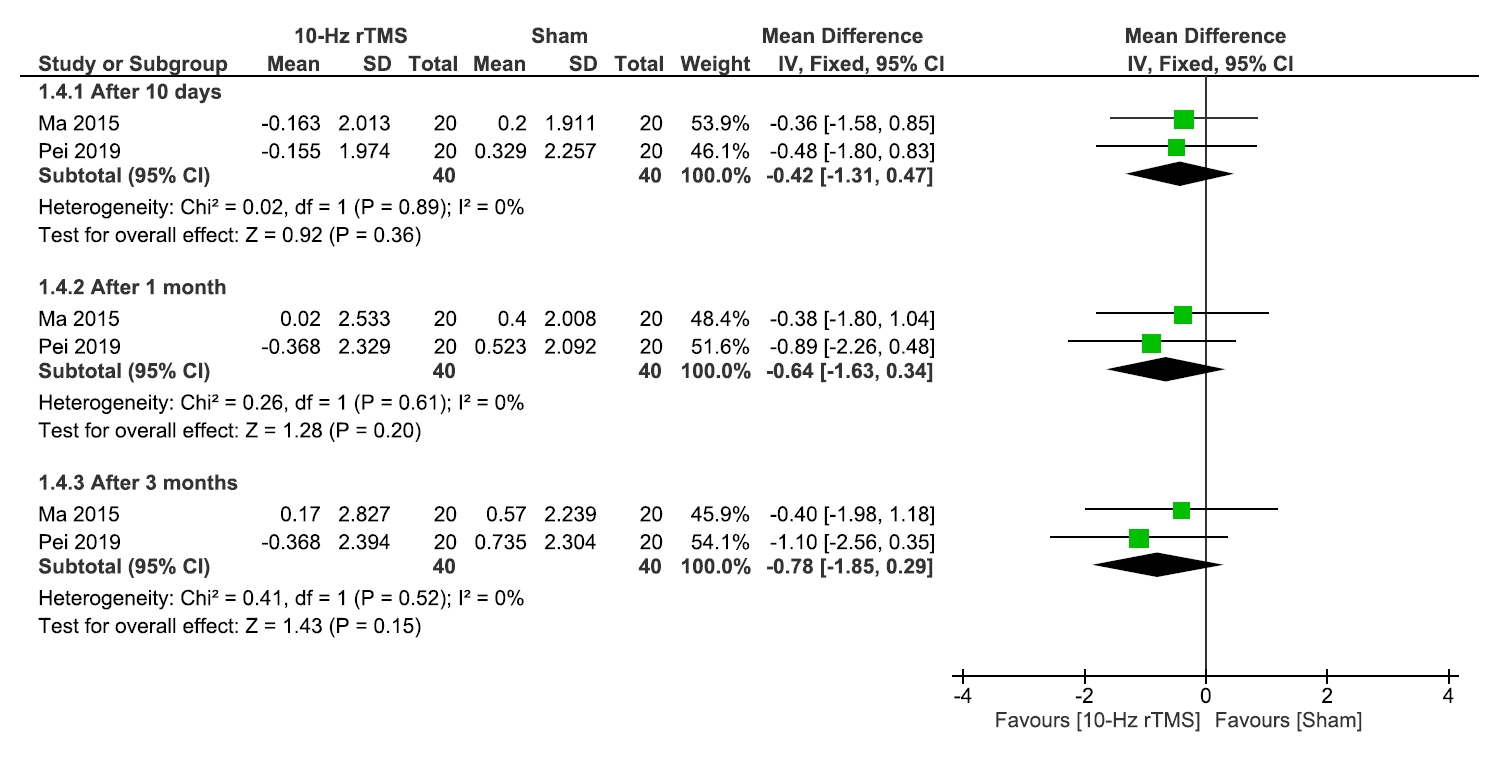
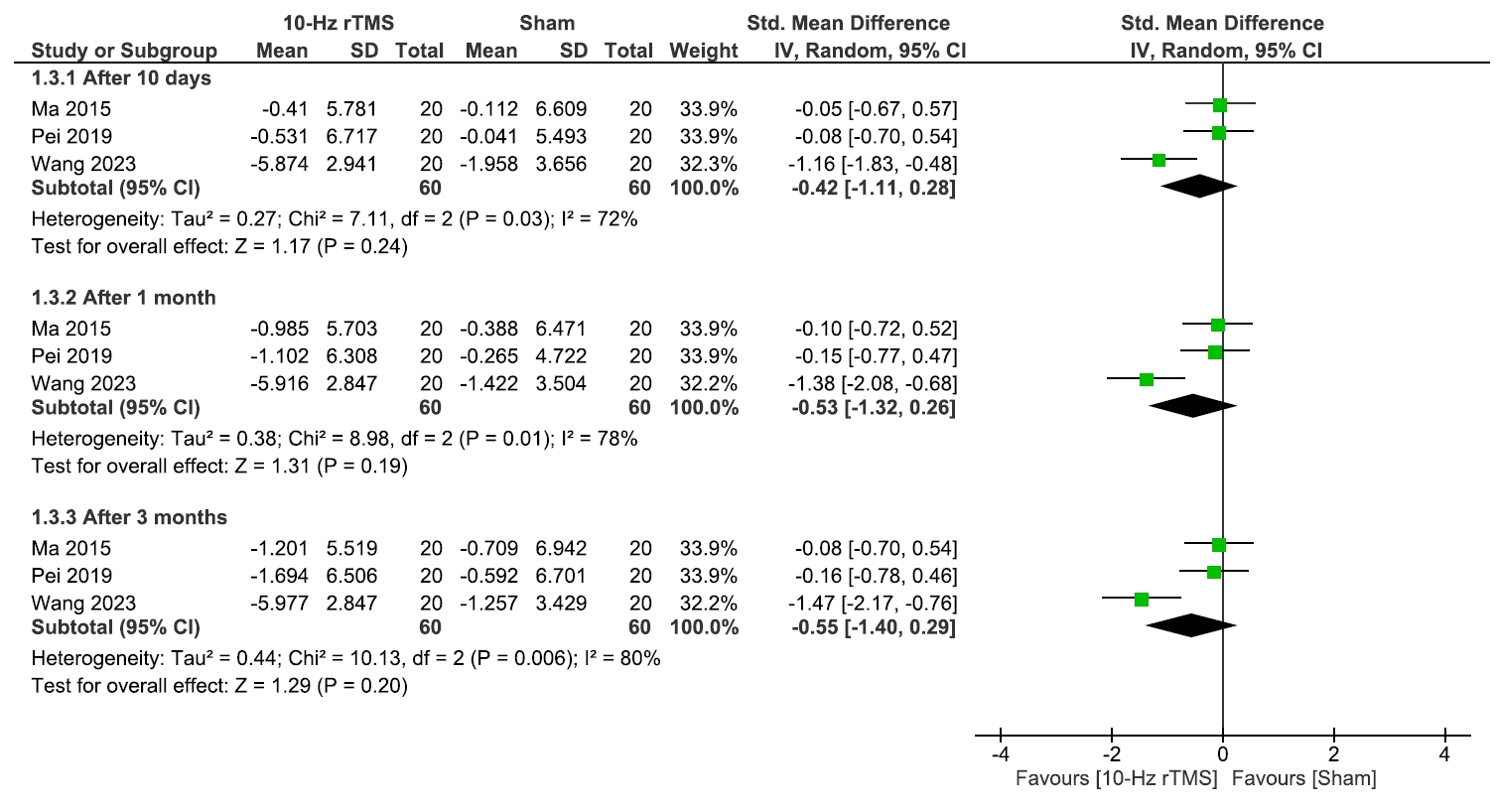
RESULTS
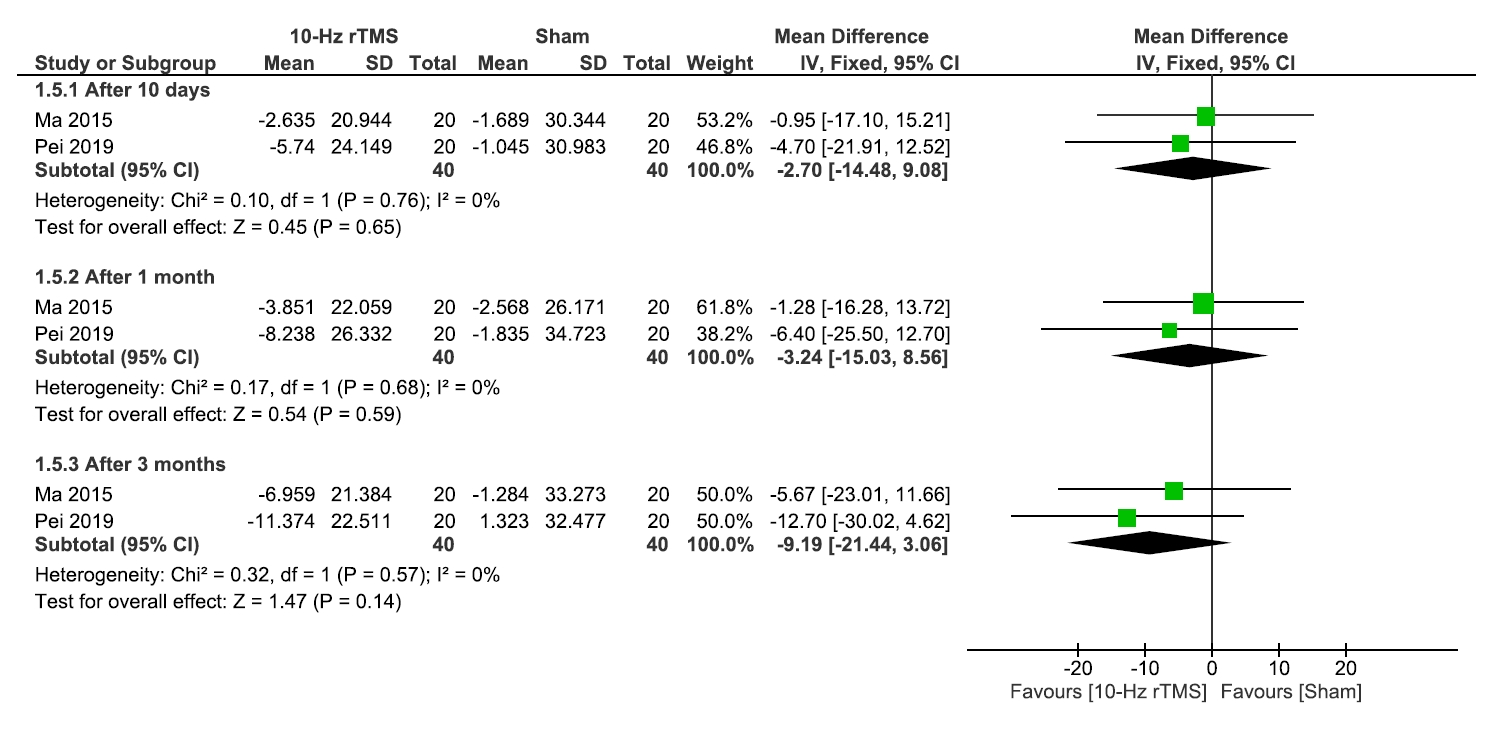
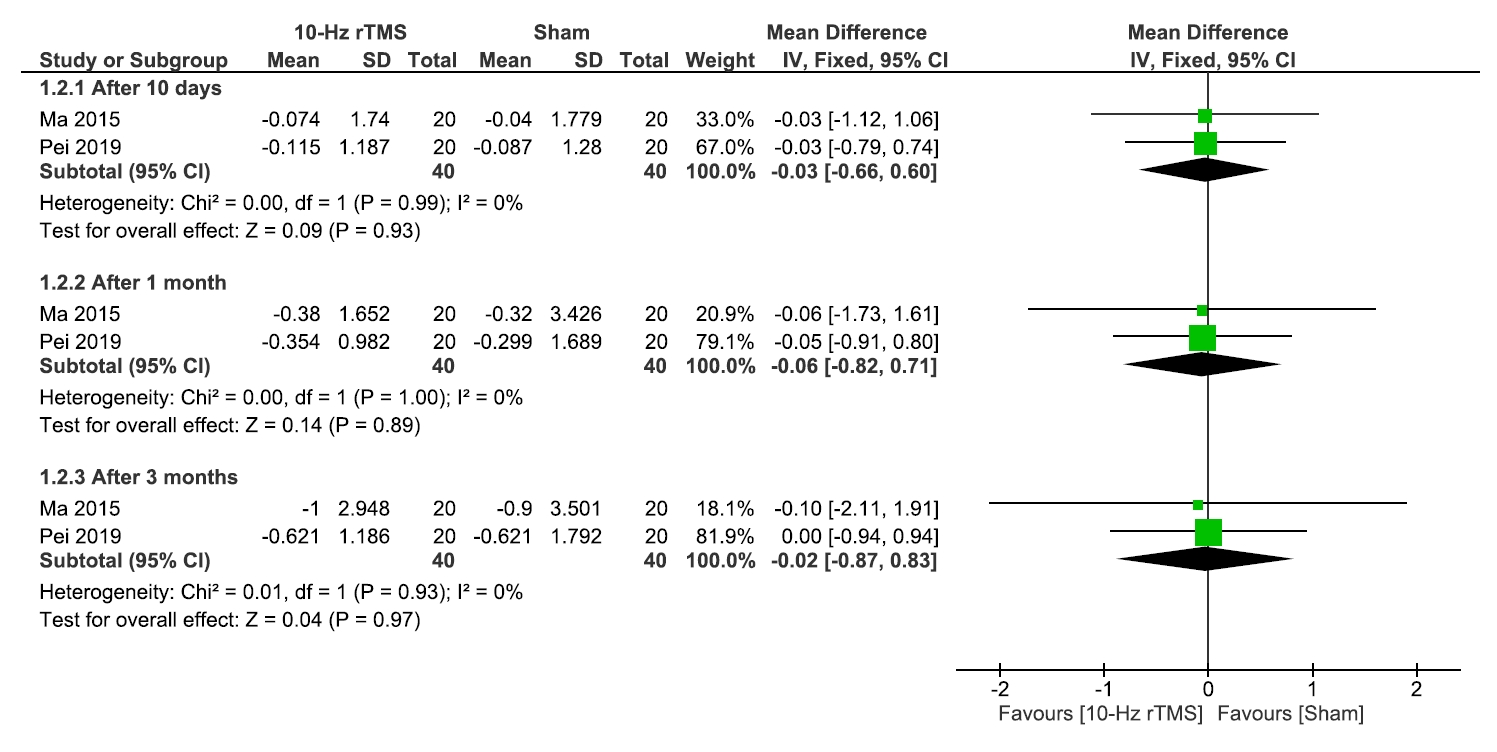
1) Sleep quality
2) Quality of life and medication regulation
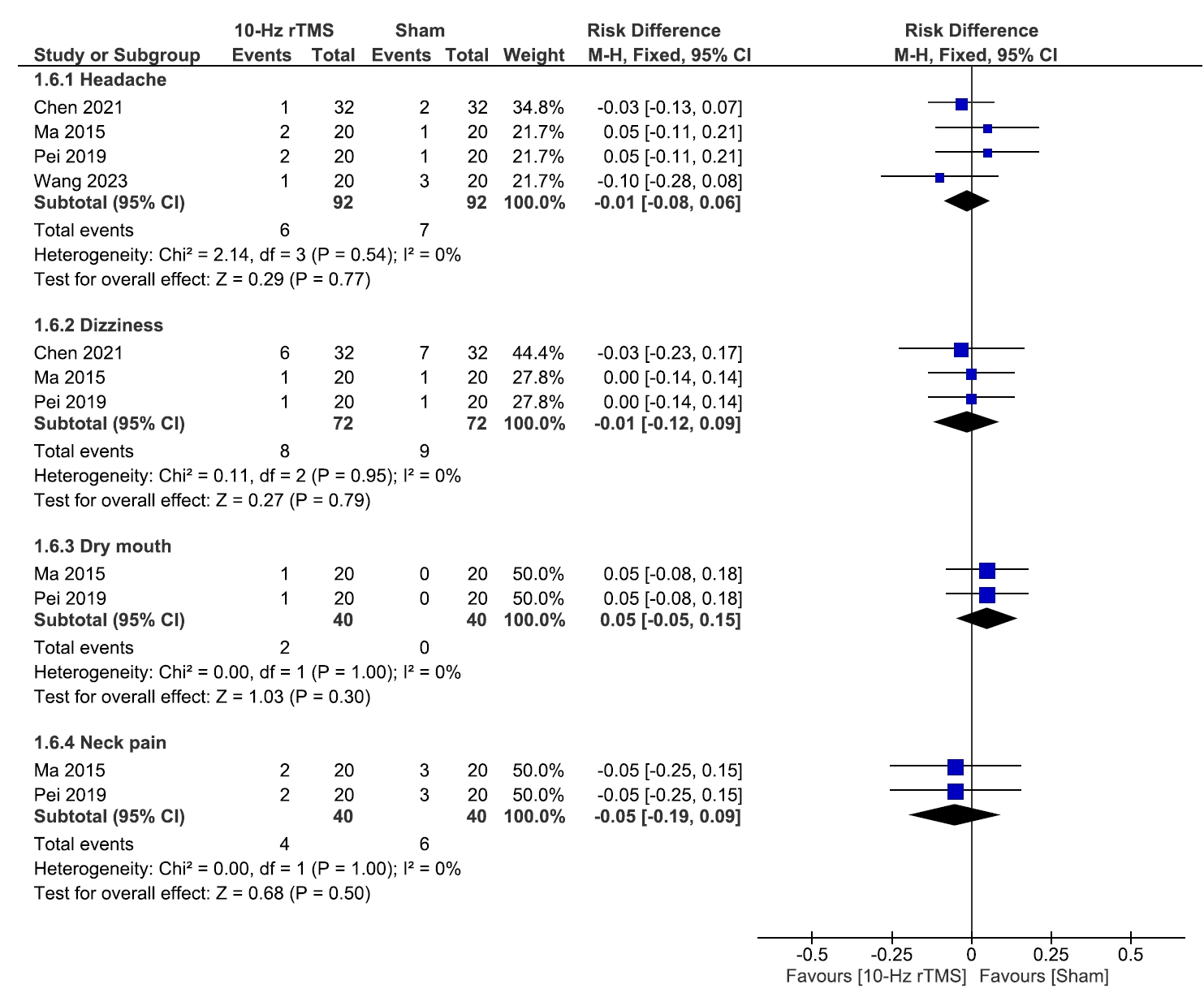
3) Adverse events
DISCUSSION
CONCLUSION
AVAILABILITY OF DATA AND MATERIAL
The data presented in this study are available upon reasonable request from the corresponding author.
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS
Conceptualization: AA, BL, MA, HMM, MEM, MAZ, HS; Data curation: HMM, MEM, MAZ, HS, DEA, AIGS, MSMS, AH, HA; Formal analysis: AA, HS; Investigation: AA, HMM, MEM, MAZ, HS, DEA, AIGS, MSMS; Methodology: AA, HMM, DEA, AIGS, AH; Validation: AA, HMM; Supervision: AMR; Writing–original draft: AA, BL, MA, HA, AMR; Writing–review & editing: AA, BL, DEA, HA, AMR.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
FUNDING STATEMENT
Not applicable.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
Not applicable.
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL
Supplementary Table 1.
Supplementary Table 2.
Supplementary Figure 1.
Supplementary Figure 2.
| Study (year) | Study design | Duration | Country |
Sample size |
rTMS frequency | Number of sessions of rTMS, and details of session | Target location | Outcomes measured | Main findings | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rTMS | Sham | |||||||||
| Ma et al.17 (2015) | RCT | 10 days stimulation+3 months FU | China | 20 | 20 | 10-Hz | 10 sessions, 300 5-second pulses with a three-second interval between trains (total 1,500 pulses/session), liquid-nitrogen-cooled circular coil | Primary motor cortex (M1), contralateral to the painful region | VAS, QoL, PGIC, sleep quality, MR and AEs | The rTMS group showed a significant reduction in VAS score compared to the Sham group. Significant improvements were found in sleep quality at T11 and higher PGIC scale in the rTMS group. No serious AEs were observed; there were only minor AEs such as dry mouth, headache, neck pain, and dizziness. |
| Pei et al.18 (2019) | RCT | 10 days+3 months FU | China | 20 | 20 | 10-Hz | 10 sessions, 300 half-second pulses with three-second intervals (total 1,500 pulses/session), total stimulation time: 17.5 minutes, 15-channel head coil | Primary motor cortex (M1), contralateral to the painful region | VAS, SF-MPQ, QoL, SQ, SDS, PGIC and AEs. | The rTMS group showed a significant reduction in VAS compared to the Sham group. The QoL, SQ, and PGIC scores of the 10-Hz rTMS group at T12 was significantly higher than that of the Sham rTMS group. No serious AEs occurred; there were only minor AEs like dry mouth, headache, neck pain, and dizziness. |
| Chen et al.20 (2021) | RCT | 2 weeks+9 months FU (follow up at 2, 6, 12, 36 weeks) | China | 32 | Gabapentin capsules and Sham rTMS: 32 | 10-Hz | 15 consecutive sessions, 1,500 pulses per session, stimulation duration: 17.5 minutes, figure-eight coil | Primary motor cortex (M1), contralateral to the painful region | VAS, AEs, SEP, AIS | The rTMS group showed significant improvements in VAS compared to the Sham group. No AEs were reported in the rTMS group. |
| Wang et al.19 (2023) | RCT | 2 weeks stimulation+3 months FU | China | 20 | 20 | 10-Hz | 10 daily sessions for 2 weeks, 3,000 pulses at 10 Hz with 5-second trains and 25-second intervals | Primary motor cortex (M1), contralateral to the painful region | VAS, SF-MPQ, PSQI, PGIC and AEs | The rTMS group showed improvements in VAS, SF-MPQ, PSQI, and PGIC compared to the Sham group. No serious AEs were noted; there were only mild headache and mild scalp discomfort. |
| Wu et al.21 (2023) | Retrospective | Jan 2019 to Jan 2021 6 weeks (from baseline to final measurement) | China | 31 | Nerve block and pregabalin: 30 | 10-Hz | 1,200 pulses, stimulation once daily for 4 weeks, stimulation duration: 20 minutes | Primary motor cortex (M1), contralateral to the painful region | VAS, TNF-a, IL-1B, IL-6, NLRP3, caspase-1, AEs | The rTMS group showed improvement in VAS and inflammatory markers compared to the sham group. No serious AEs occurred; the only AEs were mild headache and mild scalp discomfort. |
RCT, randomized controlled trial; FU, follow-up; rTMS, repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation; Sham, sham treatment (placebo control); VAS, visual analogue scale; QoL, quality of life; PGIC, patient’s global impression of change; MR, medication regulation; AEs, adverse events; SF-MPQ, Short-Form McGill Pain Questionnaire; SDS, Self-Rating Depression Scale; SQ, sleep quality; SEP, somatosensory evoked potentials; AIS, Athens Insomnia Scale; PSQI, Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index; TNF, tumor necrosis factor; IL, interleukin.
| Study (year) | Age (yr) | Male sex | Pain duration (mo) | Current medications | Painful region | Underlying disease | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rTMS | Control | rTMS | Sham | rTMS | Sham | rTMS | Sham | rTMS | Sham | rTMS | Sham | |
| Ma et al.17 (2015) | 65.4±10.5 | 67.3±11.9 | 11 (55) | 9 (45) | 17.3±24.1 | 15.7±23.2 | Gabapentin: 16 (80) | Gabapentin: 18 (90) | Upper: 9 (45) (the pain region lies at or above the upper fourth thoracic nerve distribution) | Upper: 9 (45) | HTN: 3 (15), DM: 3 (15), cardiopulmonary disease: 4 (20), cerebral infraction: 4 (20) | HTN: 4 (20), DM: 6 (30), cardiopulmonary disease: 4 (20), cerebral infraction: 4 (20) |
| Tramadol: 5 (25) | Tramadol: 8 (40) | |||||||||||
| Mecobalamin: 6 (30) | Mecobalamin: 7 (35) | |||||||||||
| Acetaminophen: 2 (10) | Acetaminophen: 3 (15) | |||||||||||
| Oxycodone: 2 (10) | Oxycodone: 3 (15) | |||||||||||
| Pei et al.18 (2019) | 65.9±12.3 | 67.3±11.9 | 10 (50) | 11 (55) | 16.5±20.4 | 15.7±23.2 | Gabapentin: 18 (90) | Gabapentin: 18 (90) | Upper: 9 (45) | Upper: 9 (45) | HTN: 3 (15), DM: 4 (20), cardiopulmonary disease: 3 (15), cerebral infraction: 5 (25) | HTN: 4 (20), DM: 6 (30), cardiopulmonary disease: 4 (20), cerebral infraction: 4 (20) |
| Tramadol: 7 (35) | Tramadol: 8 (40) | |||||||||||
| Mecobalamin: 5 (25) | Mecobalamin: 7 (35) | |||||||||||
| Acetaminophen: 3(15) | Acetaminophen: 3 (15) | |||||||||||
| Oxycodone: 2 (10) | Oxycodone: 3 (15) | |||||||||||
| Chen et al.20 (2021) | 62.7±5.8 | 61.3±4.9 | 16 (50) | 19 (59.3) | 37.2±4.8 | 31.2±6.0 | 1 patient: pregabalin 150 mg | N/A | Head: 6 (18.75) | Head: 4 (12.5) | N/A | N/A |
| 1 patient: gabapentin 600 mg | Face: 19 (59.375) | Face: 22 (68.75) | ||||||||||
| Limbs: 7 (21.875) | Limbs: 6 (18.75) | |||||||||||
| Wang et al.19 (2023) | 68.5±8.19 | 67.05±7.67 | 14 (70) | 7 (35) | 18.5±23.57 | 10.55±14.67 | Pregabalin: 16 (80) | Pregabalin: 15 (75) | Upper limbs: 2 (10) | Upper limbs: 4 (20) | N/A | N/A |
| Gabapentin: 3 (15) | Gabapentin: 3 (15) | Lower limbs: 1 (5) | Lower limbs: 1 (5) | |||||||||
| Others: 1 (5) | Others: 13 (65) | Face/head: 4 (20) | Face/head: 2 (10) | |||||||||
| Trunk: 13 (65) | Trunk: 13 (65) | |||||||||||
| Wu et al.21 (2023) | 57.45±7.69 | 57.23±7.59 | 15 (48.39) | 16 (53.3) | 12.42±2.64 | 12.06±2.66 | N/A | Pregabalin: 16 (100) | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A |
- 1. Hadley GR, Gayle JA, Ripoll J, et al. Post-herpetic neuralgia: a review. Curr Pain Headache Rep 2016;20:17.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 2. Chen F, Chen F, Shang Z, et al. White matter microstructure degenerates in patients with postherpetic neuralgia. Neurosci Lett 2017;656:152-157.ArticlePubMed
- 3. Nair PA, Patel BC. Herpes Zoster. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. 2023.
- 4. Thomas SL, Hall AJ. What does epidemiology tell us about risk factors for herpes zoster? Lancet Infect Dis 2004;4:26-33.ArticlePubMed
- 5. Drolet M, Brisson M, Schmader KE, et al. The impact of herpes zoster and postherpetic neuralgia on health-related quality of life: a prospective study. CMAJ 2010;182:1731-1736.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 6. Saguil A, Kane S, Mercado M, Lauters R. Herpes zoster and postherpetic neuralgia: prevention and management. Am Fam Physician 2017;96:656-663.PubMedPDF
- 7. Lefaucheur JP, Aleman A, Baeken C, et al. Evidence-based guidelines on the therapeutic use of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS): an update (2014-2018). Clin Neurophysiol 2020;131:474-528.ArticlePubMed
- 8. Picarelli H, Teixeira MJ, de Andrade DC, et al. Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation is efficacious as an add-on to pharmacological therapy in complex regional pain syndrome (CRPS) type I. J Pain 2010;11:1203-1210.ArticlePubMed
- 9. Passard A, Attal N, Benadhira R, et al. Effects of unilateral repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation of the motor cortex on chronic widespread pain in fibromyalgia. Brain 2007;130:2661-2670.ArticlePubMed
- 10. Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021;372:n71.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 11. Higgins JPT, Thomas J, Chandler J. Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions version 6.5 [Internet]. Cochrane; 2024 [cited 2024 Jul 12]. Available from: https://handbook-5-1.cochrane.org/chapter_9/9_2_3_2_the_standardized_mean_difference.htm
- 12. Rayyan. Intelligent systematic review - Rayyan [Internet]. Rayyan; 2024 [cited 2024 Jul 12]. Available from: https://www.rayyan.ai/
- 13. Sterne JAC, Savović J, Page MJ, et al. RoB 2: a revised tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ 2019;366:l4898.ArticlePubMed
- 14. Wells GA, Shea B, O’Connell D, et al. The Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) for assessing the quality of nonrandomised studies in meta-analyses [Internet]. Ottawa Hospital Research Institute; 2024 [cited 2024 Jul 12]. Available from: https://www.ohri.ca/programs/clinical_epidemiology/oxford.asp
- 15. Abbas A, Hefnawy MT, Negida A, et al. Meta-analysis accelerator: a comprehensive tool for statistical data conversion in systematic reviews with meta-analysis. BMC Med Res Methodol 2024;24:243.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 16. Higgins JPT, Green S. 10.4.3.1 Recommendations on testing for funnel plot asymmetry [Internet]. The Cochrane Collaboration; 2021 [cited 2024 Aug 10]. Available from: https://handbook-5-1.cochrane.org/chapter_10/10_4_3_1_recommendations_on_testing_for_funnel_plot_asymmetry.htm
- 17. Ma SM, Ni JX, Li XY, Yang LQ, Guo YN, Tang YZ. High-frequency repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation reduces pain in postherpetic neuralgia. Pain Med 2015;16:2162-2170.ArticlePubMed
- 18. Pei Q, Wu B, Tang Y, et al. Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation at different frequencies for postherpetic neuralgia: a double-blind, sham-controlled, randomized trial. Pain Physician 2019;22:E303-E313.ArticlePubMed
- 19. Wang H, Hu Y, Deng J, et al. A randomised sham-controlled study evaluating rTMS analgesic efficacy for postherpetic neuralgia. Front Neurosci 2023;17:1158737.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 20. Chen X, Liao P, Shi Q, et al. Short-and long-term effects of yiqihuoxuezhitong decoction combined high frequency repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation on pain and sleep quality in elderly patients with postherpetic neuralgia. Chin Gen Pract 2021;24:2174-2178.Article
- 21. Wu Z, Liu Q. Effects of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation combined with acupuncture on NLRP3 inflammasome and protease levels in patients with neuropathic pain. Am J Transl Res 2023;15:4699-4708.PubMedPMC
- 22. Goto T, Saitoh Y, Hashimoto N, et al. Diffusion tensor fiber tracking in patients with central post-stroke pain; correlation with efficacy of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation. Pain 2008;140:509-518.ArticlePubMed
- 23. Ahmed MA, Mohamed SA, Sayed D. Long-term antalgic effects of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation of motor cortex and serum beta-endorphin in patients with phantom pain. Neurol Res 2011;33:953-958.ArticlePubMed
- 24. Clarke D, Beros J, Bates KA, Harvey AR, Tang AD, Rodger J. Low intensity repetitive magnetic stimulation reduces expression of genes related to inflammation and calcium signalling in cultured mouse cortical astrocytes. Brain Stimul 2021;14:183-191.ArticlePubMed
- 25. Kinney KR, Hanlon CA. Changing cerebral blood flow, glucose metabolism, and dopamine binding through transcranial magnetic stimulation: a systematic review of transcranial magnetic stimulation-positron emission tomography literature. Pharmacol Rev 2022;74:918-932.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 26. Moisset X, de Andrade DC, Bouhassira D. From pulses to pain relief: an update on the mechanisms of rTMS-induced analgesic effects. Eur J Pain 2016;20:689-700.ArticlePubMed
- 27. Che X, Fitzgibbon BM, Ye Y, et al. Characterising the optimal pulse number and frequency for inducing analgesic effects with motor cortex rTMS. Brain Stimul 2021;14:1081-1083.ArticlePubMed
- 28. Borckardt JJ, Smith AR, Reeves ST, et al. A pilot study investigating the effects of fast left prefrontal rTMS on chronic neuropathic pain. Pain Med 2009;10:840-849.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 29. Martin L, Borckardt JJ, Reeves ST, et al. A pilot functional MRI study of the effects of prefrontal rTMS on pain perception. Pain Med 2013;14:999-1009.ArticlePubMed
- 30. Tracey I, Mantyh PW. The cerebral signature for pain perception and its modulation. Neuron 2007;55:377-391.ArticlePubMed
- 31. Attal N, Poindessous-Jazat F, De Chauvigny E, et al. Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation for neuropathic pain: a randomized multicentre sham-controlled trial. Brain 2021;144:3328-3339.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 32. Argoff CE. Review of current guidelines on the care of postherpetic neuralgia. Postgrad Med 2011;123:134-142.ArticlePubMed
- 33. Raja SN, Haythornthwaite JA, Pappagallo M, et al. Opioids versus antidepressants in postherpetic neuralgia: a randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Neurology 2002;59:1015-1021.ArticlePubMed
- 34. Derry S, Rice AS, Cole P, Tan T, Moore RA. Topical capsaicin (high concentration) for chronic neuropathic pain in adults. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2017;1:CD007393.ArticlePubMed
- 35. Argoff CE, Katz N, Backonja M. Treatment of postherpetic neuralgia: a review of therapeutic options. J Pain Symptom Manage 2004;28:396-411.ArticlePubMed
- 36. Kurklinsky S, Palmer SC, Arroliga MJ, Ghazi SM. Neuromodulation in postherpetic neuralgia: case reports and review of the literature. Pain Med 2018;19:1237-1244.ArticlePubMed
- 37. Gan EY, Tian EA, Tey HL. Management of herpes zoster and post-herpetic neuralgia. Am J Clin Dermatol 2013;14:77-85.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 38. Abbas A, Abouelmagd M, El-Moslemani M. Assessing the efficacy of spinal cord stimulation in managing painful diabetic neuropathy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Neuromodulation 2025 Mar 6 [Epub]. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurom.2025.01.016.ArticlePubMed
- 39. Barbarisi M, Pace MC, Passavanti MB, et al. Pregabalin and transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation for postherpetic neuralgia treatment. Clin J Pain 2010;26:567-572.ArticlePubMed
- 40. Stepanović A, Kolšek M, Kersnik J, Erčulj V. Prevention of post-herpetic neuralgia using transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation. Wien Klin Wochenschr 2015;127:369-374.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 41. Ding Y, Yao P, Li H, et al. CT-guided stellate ganglion pulsed radiofrequency stimulation for facial and upper limb postherpetic neuralgia. Front Neurosci 2019;13:170.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 42. Li M, Hu H, Tong SX, et al. The therapeutic efficacy of pulsed radiofrequency alone versus a dexamethasone and pulsed radiofrequency combination in patients with trigeminal postherpetic neuralgia: a double-blind, randomized controlled trial. Pain Physician 2022;25:E543-E549.PubMedPDF
- 43. Apalla Z, Sotiriou E, Lallas A, Lazaridou E, Ioannides D. Botulinum toxin A in postherpetic neuralgia: a parallel, randomized, double-blind, single-dose, placebo-controlled trial. Clin J Pain 2013;29:857-864.ArticlePubMed
- 44. Tringali S, Perrot X, Collet L, Moulin A. Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation: hearing safety considerations. Brain Stimul 2012;5:354-363.ArticlePubMed
- 45. Overvliet GM, Jansen RAC, van Balkom AJLM, et al. Adverse events of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation in older adults with depression, a systematic review of the literature. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry 2021;36:383-392.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 46. Lerner AJ, Wassermann EM, Tamir DI. Seizures from transcranial magnetic stimulation 2012-2016: results of a survey of active laboratories and clinics. Clin Neurophysiol 2019;130:1409-1416.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 47. Dai Q, Xu A, Wang K, Yang Y, Shao Y, Sun Y. The efficacy of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation in postherpetic neuralgia: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Front Neurol 2024;15:1365445.ArticlePubMedPMC
REFERENCES
Figure & Data
References
Citations

 PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link-
 Cite this Article
Cite this Article
- Cite this Article
-
- Close
- Download Citation
- Close
- Figure
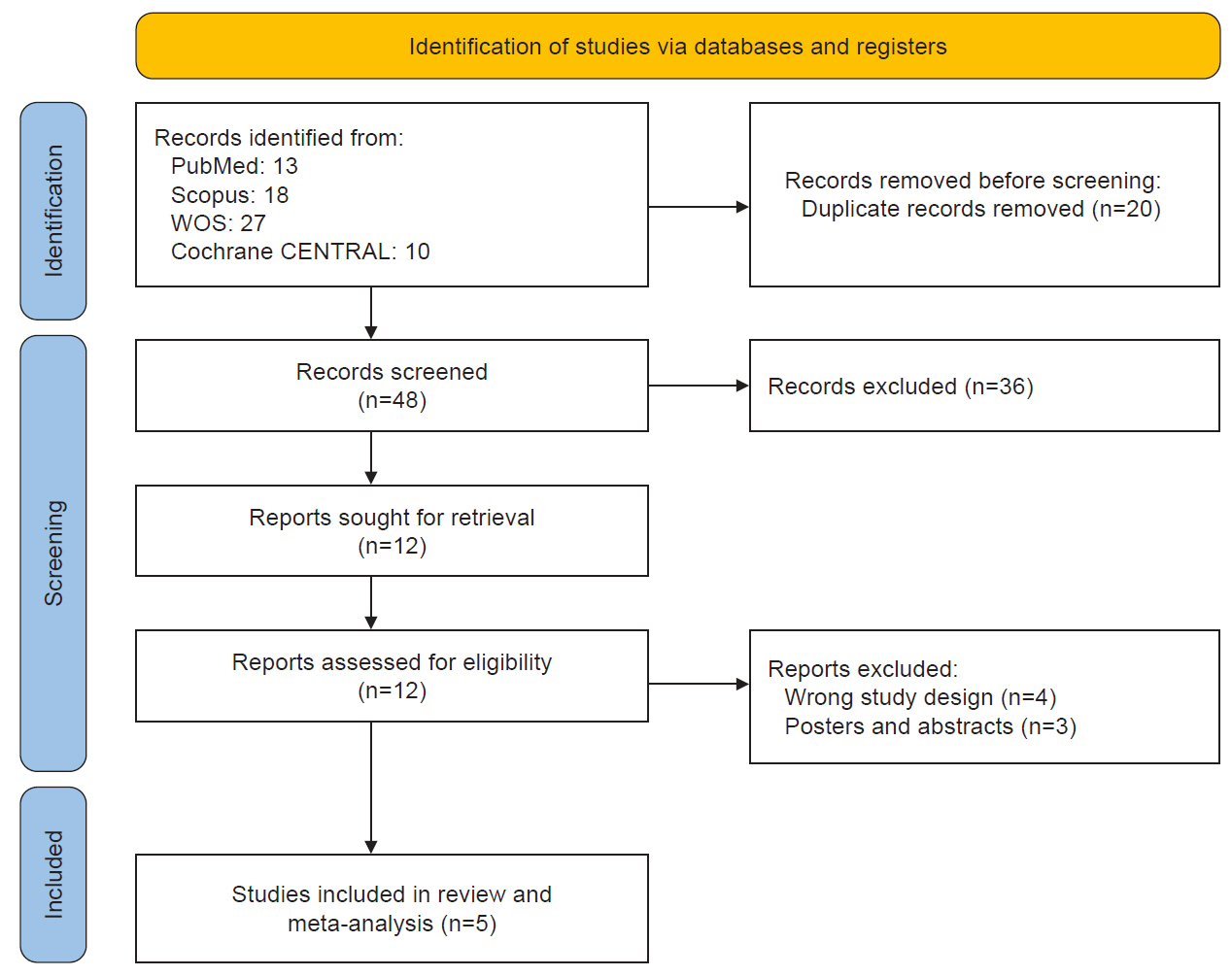
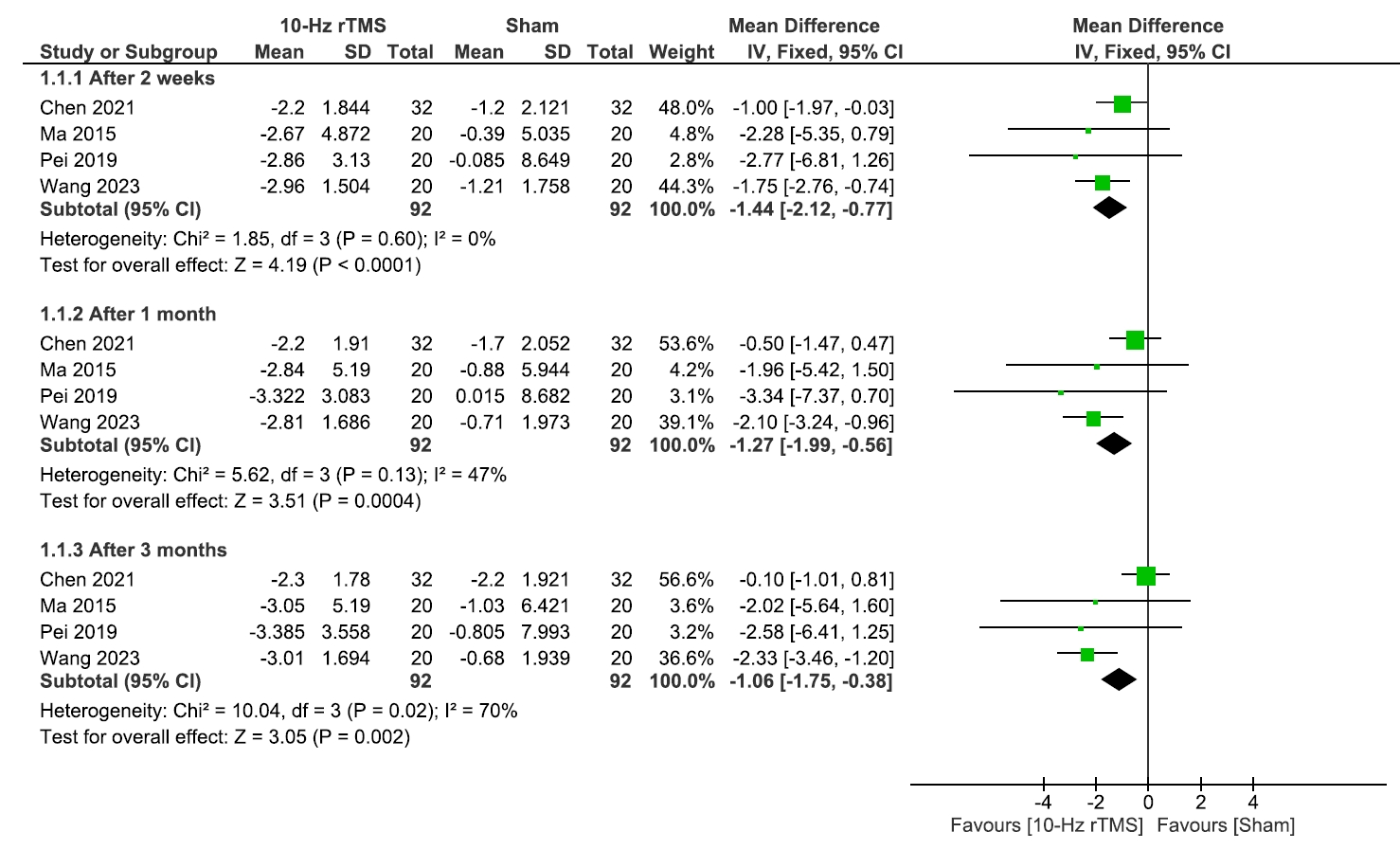
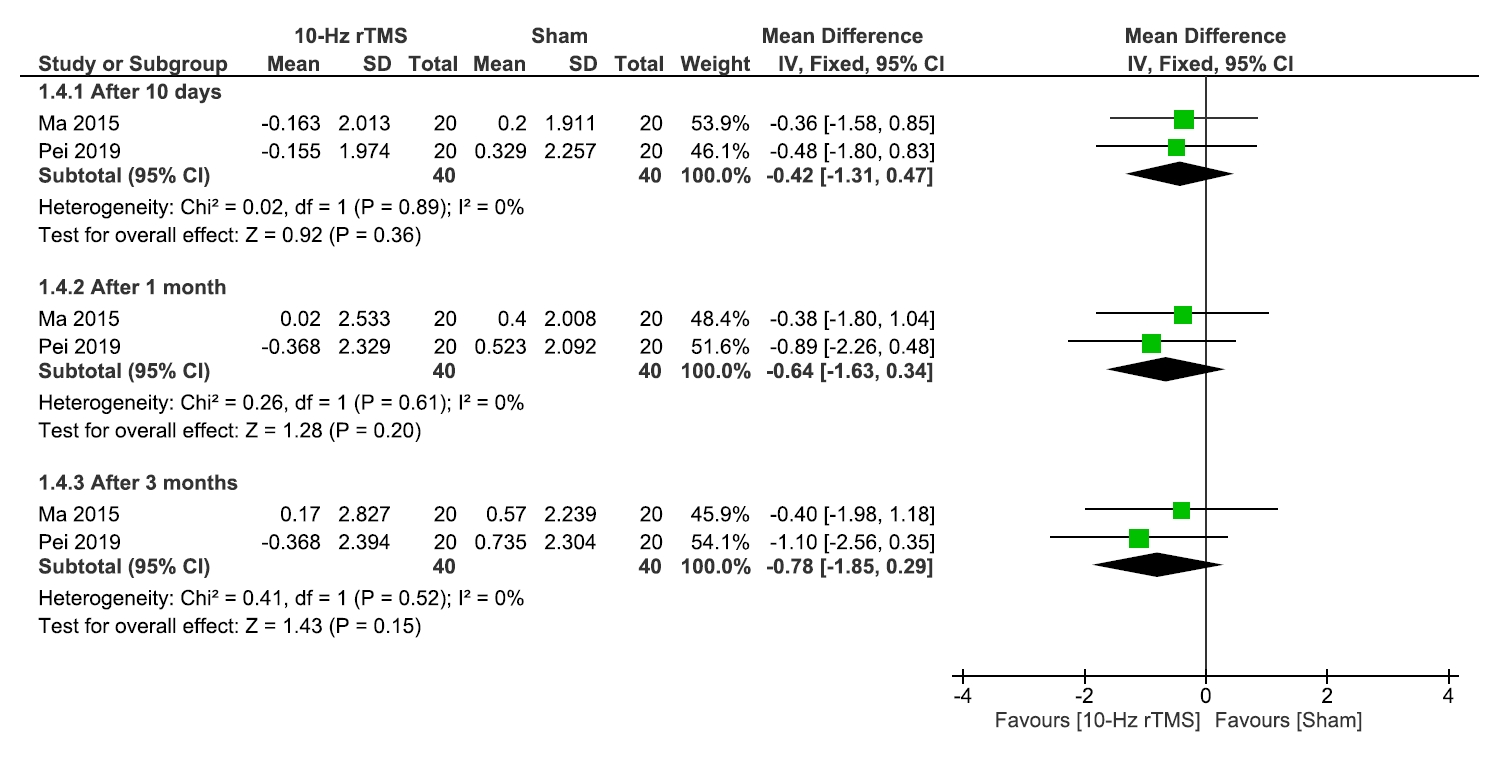
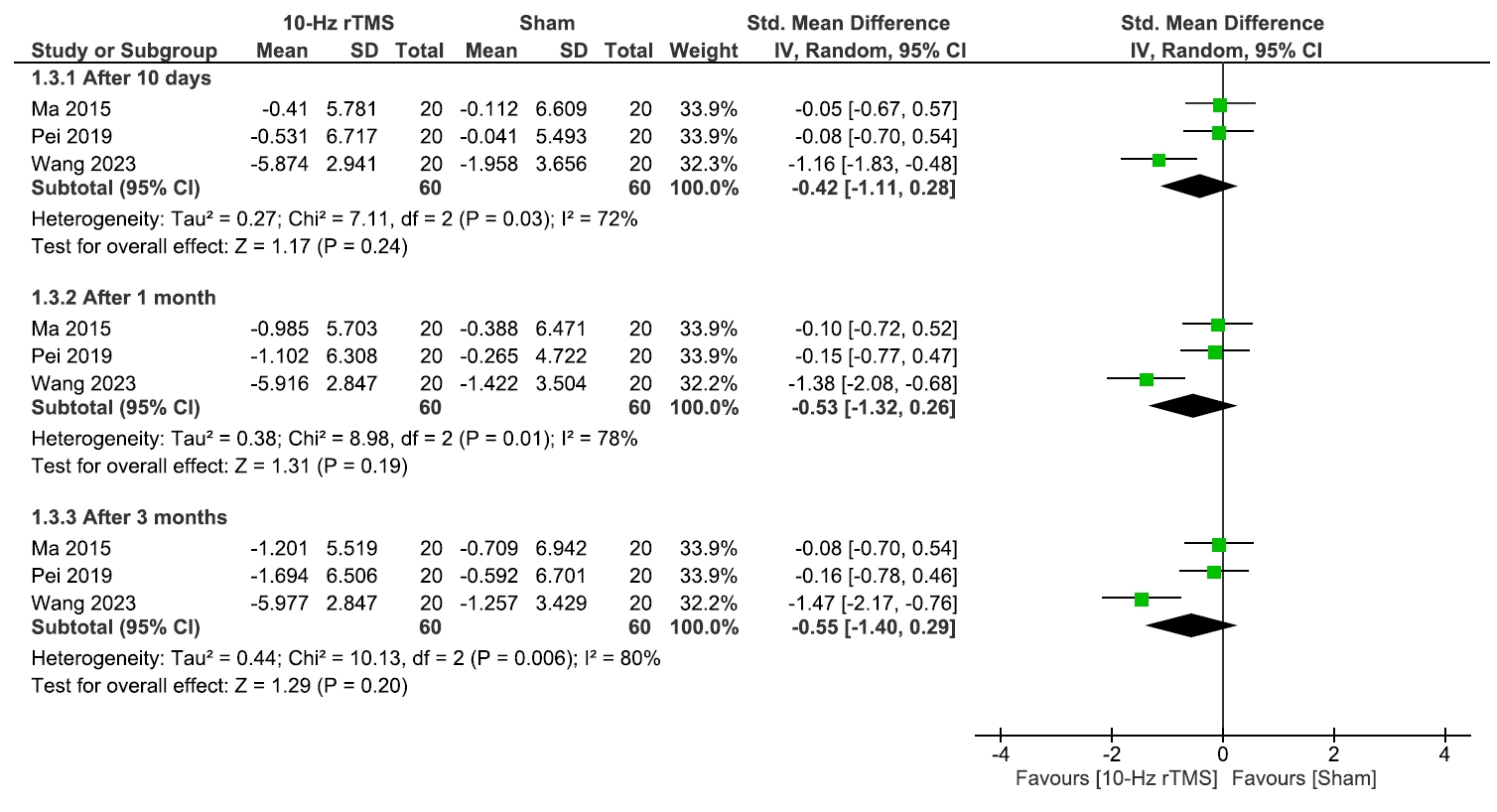
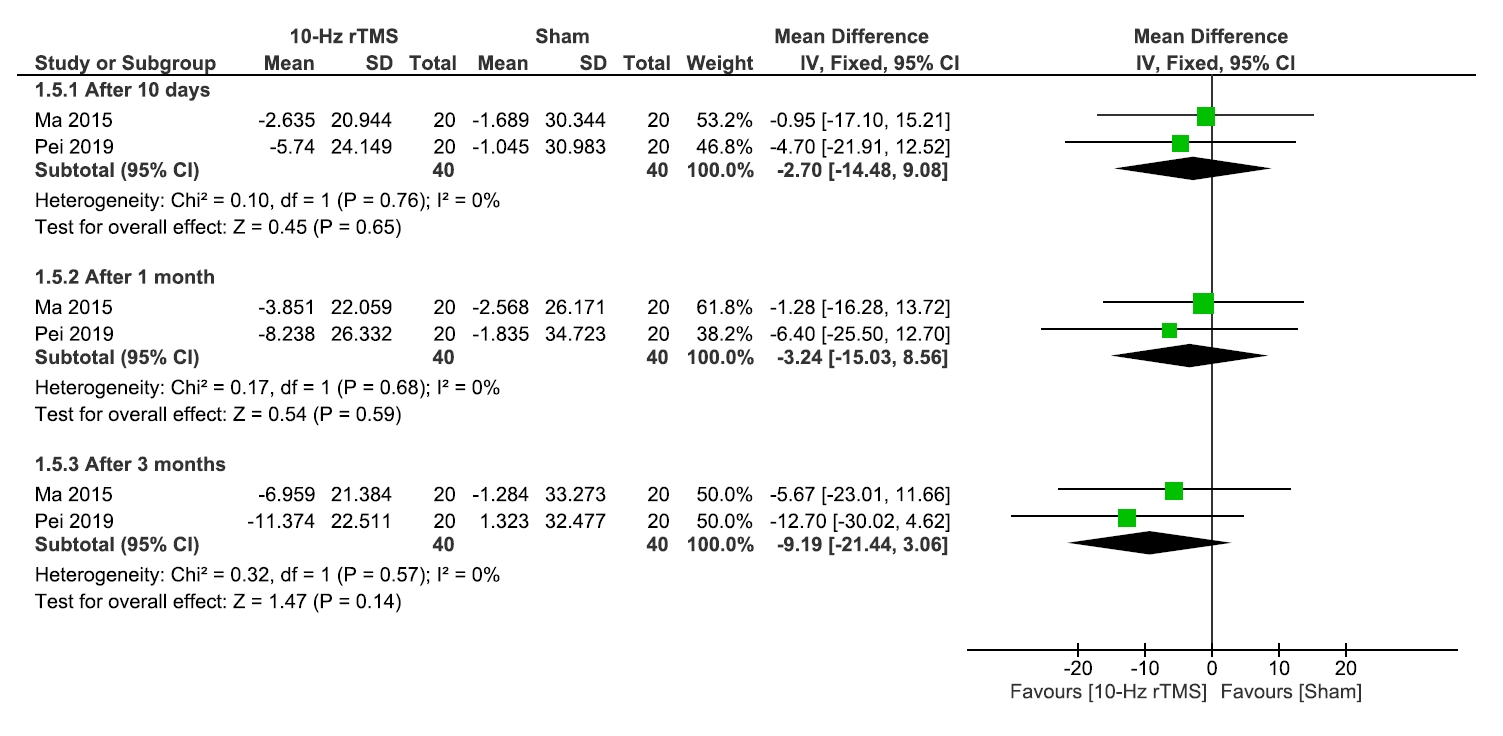
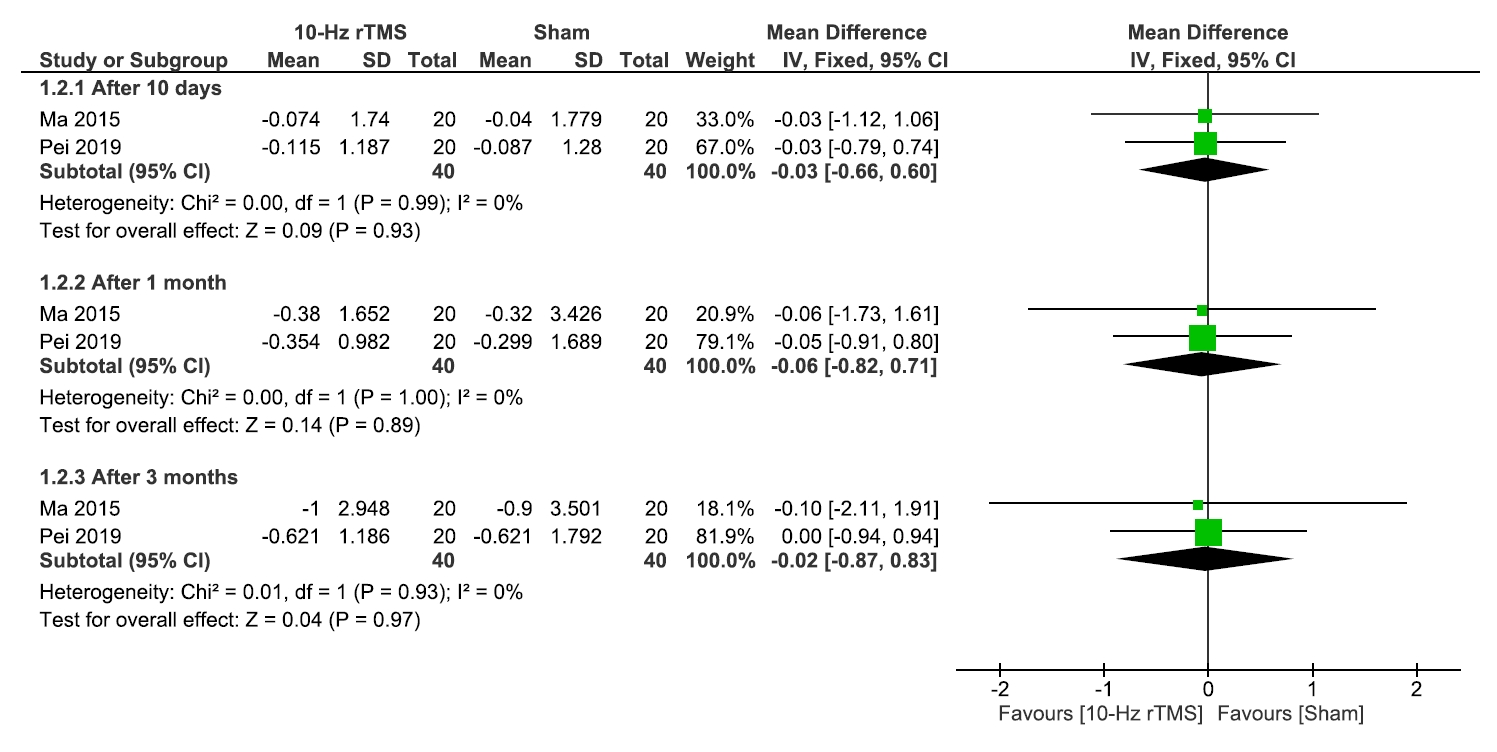
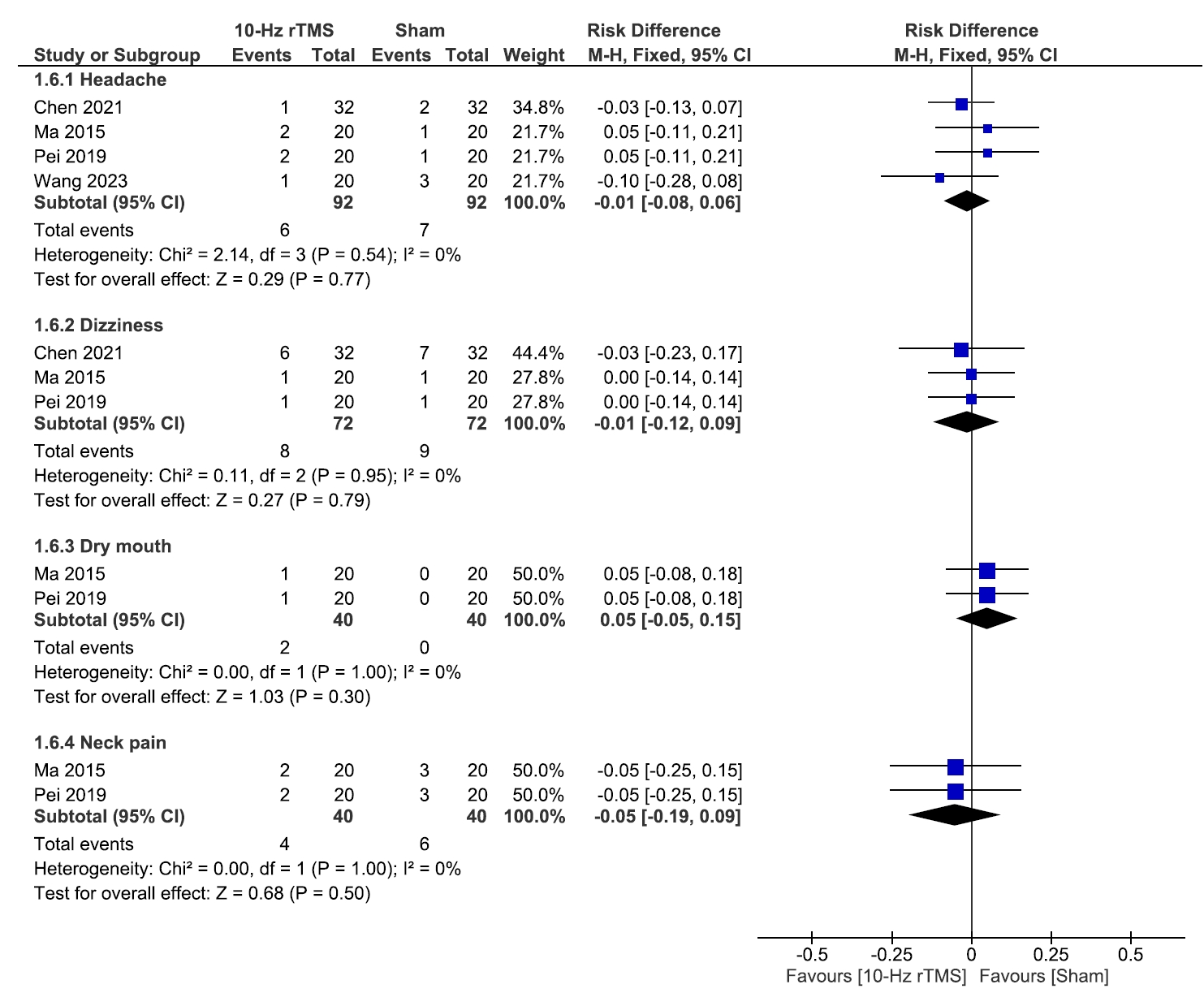
Figure 1.
Figure 2.
Figure 3.
Figure 4.
Figure 5.
Figure 6.
Figure 7.
| Study (year) | Study design | Duration | Country | Sample size |
rTMS frequency | Number of sessions of rTMS, and details of session | Target location | Outcomes measured | Main findings | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rTMS | Sham | |||||||||
| Ma et al.17 (2015) | RCT | 10 days stimulation+3 months FU | China | 20 | 20 | 10-Hz | 10 sessions, 300 5-second pulses with a three-second interval between trains (total 1,500 pulses/session), liquid-nitrogen-cooled circular coil | Primary motor cortex (M1), contralateral to the painful region | VAS, QoL, PGIC, sleep quality, MR and AEs | The rTMS group showed a significant reduction in VAS score compared to the Sham group. Significant improvements were found in sleep quality at T11 and higher PGIC scale in the rTMS group. No serious AEs were observed; there were only minor AEs such as dry mouth, headache, neck pain, and dizziness. |
| Pei et al.18 (2019) | RCT | 10 days+3 months FU | China | 20 | 20 | 10-Hz | 10 sessions, 300 half-second pulses with three-second intervals (total 1,500 pulses/session), total stimulation time: 17.5 minutes, 15-channel head coil | Primary motor cortex (M1), contralateral to the painful region | VAS, SF-MPQ, QoL, SQ, SDS, PGIC and AEs. | The rTMS group showed a significant reduction in VAS compared to the Sham group. The QoL, SQ, and PGIC scores of the 10-Hz rTMS group at T12 was significantly higher than that of the Sham rTMS group. No serious AEs occurred; there were only minor AEs like dry mouth, headache, neck pain, and dizziness. |
| Chen et al.20 (2021) | RCT | 2 weeks+9 months FU (follow up at 2, 6, 12, 36 weeks) | China | 32 | Gabapentin capsules and Sham rTMS: 32 | 10-Hz | 15 consecutive sessions, 1,500 pulses per session, stimulation duration: 17.5 minutes, figure-eight coil | Primary motor cortex (M1), contralateral to the painful region | VAS, AEs, SEP, AIS | The rTMS group showed significant improvements in VAS compared to the Sham group. No AEs were reported in the rTMS group. |
| Wang et al.19 (2023) | RCT | 2 weeks stimulation+3 months FU | China | 20 | 20 | 10-Hz | 10 daily sessions for 2 weeks, 3,000 pulses at 10 Hz with 5-second trains and 25-second intervals | Primary motor cortex (M1), contralateral to the painful region | VAS, SF-MPQ, PSQI, PGIC and AEs | The rTMS group showed improvements in VAS, SF-MPQ, PSQI, and PGIC compared to the Sham group. No serious AEs were noted; there were only mild headache and mild scalp discomfort. |
| Wu et al.21 (2023) | Retrospective | Jan 2019 to Jan 2021 6 weeks (from baseline to final measurement) | China | 31 | Nerve block and pregabalin: 30 | 10-Hz | 1,200 pulses, stimulation once daily for 4 weeks, stimulation duration: 20 minutes | Primary motor cortex (M1), contralateral to the painful region | VAS, TNF-a, IL-1B, IL-6, NLRP3, caspase-1, AEs | The rTMS group showed improvement in VAS and inflammatory markers compared to the sham group. No serious AEs occurred; the only AEs were mild headache and mild scalp discomfort. |
| Study (year) | Age (yr) | Male sex | Pain duration (mo) | Current medications | Painful region | Underlying disease | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rTMS | Control | rTMS | Sham | rTMS | Sham | rTMS | Sham | rTMS | Sham | rTMS | Sham | |
| Ma et al.17 (2015) | 65.4±10.5 | 67.3±11.9 | 11 (55) | 9 (45) | 17.3±24.1 | 15.7±23.2 | Gabapentin: 16 (80) | Gabapentin: 18 (90) | Upper: 9 (45) (the pain region lies at or above the upper fourth thoracic nerve distribution) | Upper: 9 (45) | HTN: 3 (15), DM: 3 (15), cardiopulmonary disease: 4 (20), cerebral infraction: 4 (20) | HTN: 4 (20), DM: 6 (30), cardiopulmonary disease: 4 (20), cerebral infraction: 4 (20) |
| Tramadol: 5 (25) | Tramadol: 8 (40) | |||||||||||
| Mecobalamin: 6 (30) | Mecobalamin: 7 (35) | |||||||||||
| Acetaminophen: 2 (10) | Acetaminophen: 3 (15) | |||||||||||
| Oxycodone: 2 (10) | Oxycodone: 3 (15) | |||||||||||
| Pei et al.18 (2019) | 65.9±12.3 | 67.3±11.9 | 10 (50) | 11 (55) | 16.5±20.4 | 15.7±23.2 | Gabapentin: 18 (90) | Gabapentin: 18 (90) | Upper: 9 (45) | Upper: 9 (45) | HTN: 3 (15), DM: 4 (20), cardiopulmonary disease: 3 (15), cerebral infraction: 5 (25) | HTN: 4 (20), DM: 6 (30), cardiopulmonary disease: 4 (20), cerebral infraction: 4 (20) |
| Tramadol: 7 (35) | Tramadol: 8 (40) | |||||||||||
| Mecobalamin: 5 (25) | Mecobalamin: 7 (35) | |||||||||||
| Acetaminophen: 3(15) | Acetaminophen: 3 (15) | |||||||||||
| Oxycodone: 2 (10) | Oxycodone: 3 (15) | |||||||||||
| Chen et al.20 (2021) | 62.7±5.8 | 61.3±4.9 | 16 (50) | 19 (59.3) | 37.2±4.8 | 31.2±6.0 | 1 patient: pregabalin 150 mg | N/A | Head: 6 (18.75) | Head: 4 (12.5) | N/A | N/A |
| 1 patient: gabapentin 600 mg | Face: 19 (59.375) | Face: 22 (68.75) | ||||||||||
| Limbs: 7 (21.875) | Limbs: 6 (18.75) | |||||||||||
| Wang et al.19 (2023) | 68.5±8.19 | 67.05±7.67 | 14 (70) | 7 (35) | 18.5±23.57 | 10.55±14.67 | Pregabalin: 16 (80) | Pregabalin: 15 (75) | Upper limbs: 2 (10) | Upper limbs: 4 (20) | N/A | N/A |
| Gabapentin: 3 (15) | Gabapentin: 3 (15) | Lower limbs: 1 (5) | Lower limbs: 1 (5) | |||||||||
| Others: 1 (5) | Others: 13 (65) | Face/head: 4 (20) | Face/head: 2 (10) | |||||||||
| Trunk: 13 (65) | Trunk: 13 (65) | |||||||||||
| Wu et al.21 (2023) | 57.45±7.69 | 57.23±7.59 | 15 (48.39) | 16 (53.3) | 12.42±2.64 | 12.06±2.66 | N/A | Pregabalin: 16 (100) | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A |
RCT, randomized controlled trial; FU, follow-up; rTMS, repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation; Sham, sham treatment (placebo control); VAS, visual analogue scale; QoL, quality of life; PGIC, patient’s global impression of change; MR, medication regulation; AEs, adverse events; SF-MPQ, Short-Form McGill Pain Questionnaire; SDS, Self-Rating Depression Scale; SQ, sleep quality; SEP, somatosensory evoked potentials; AIS, Athens Insomnia Scale; PSQI, Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index; TNF, tumor necrosis factor; IL, interleukin.
Values are presented as mean±standard deviation or number (%). rTMS, repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation; N/A, not available; HTN, hypertension; DM, diabetes mellitus.
Table 1.
Table 2.
TOP
 KHS
KHS










