| Volume 26(3); October 2025
Full PDF
|
http://e-hpr.org |
Dear Colleagues,
We are pleased to announce the publication of the third issue of Headache and Pain Research.
Please find below the link to the table of contents and summaries of the esteemed articles.
Please enjoy, share and cite them.
Thank you for your support and assistance.
Office of Headache and Pain Research
Soo-Jin Cho, Editor-in-Chief; Soo-Kyoung Kim, Deputy Editor
| Editorial | ||
|
Toward Precision Migraine Care: Genetics, Symptoms, and Big-Data-Driven Approaches |
||
| Soo-Jin Cho | ||
| DOI: http://doi.org/10.62087/hpr.2025.0017 | ||
|
|
||
| Review Articles | ||
|
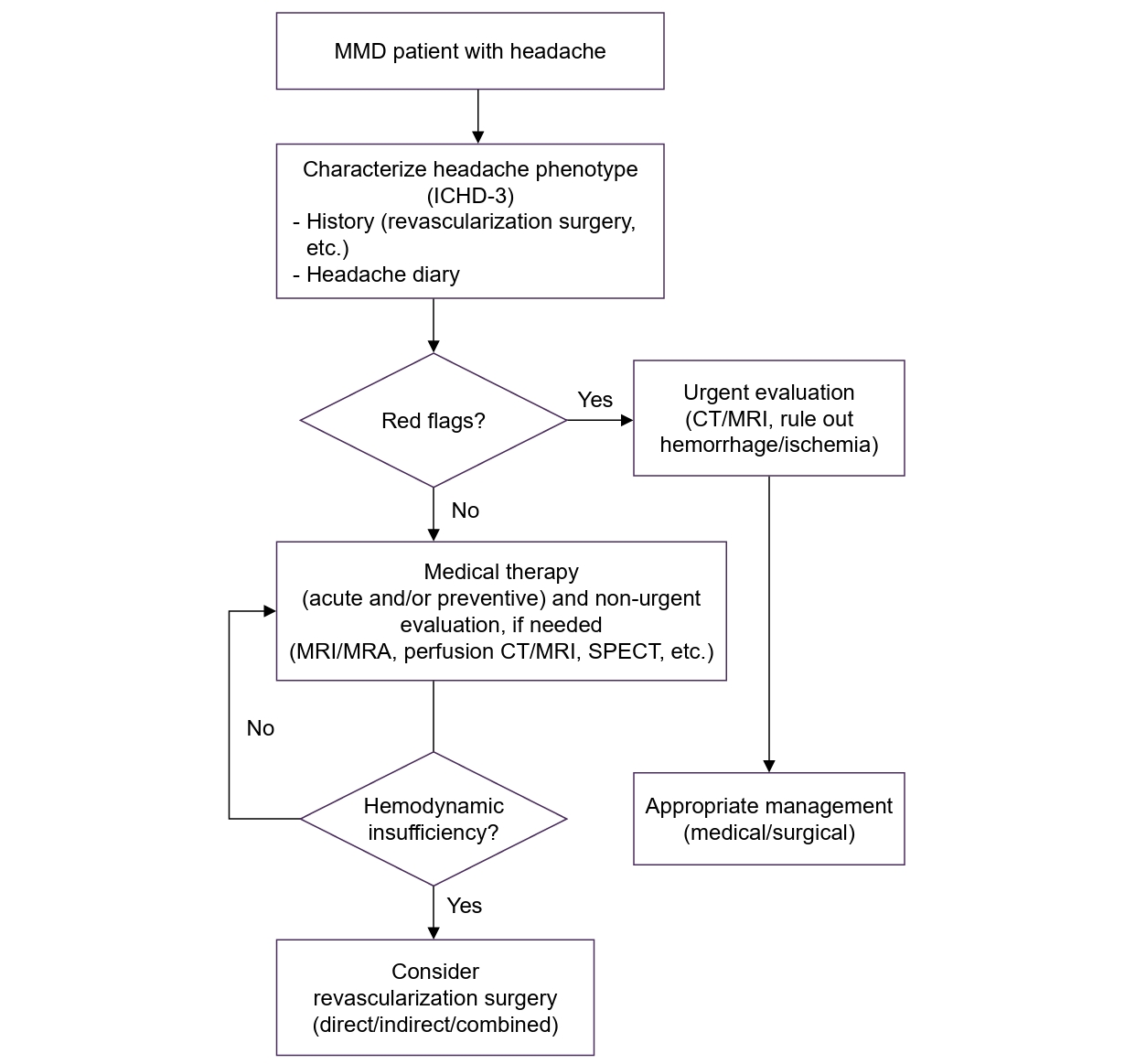
A Practical Approach to Headache in Moyamoya Disease |
||
| Mi-Yeon Eun, Jin-Man Jung, Jay Chol Choi | ||
| DOI: http://doi.org/10.62087/hpr.2025.0011 | ||
|
||
|
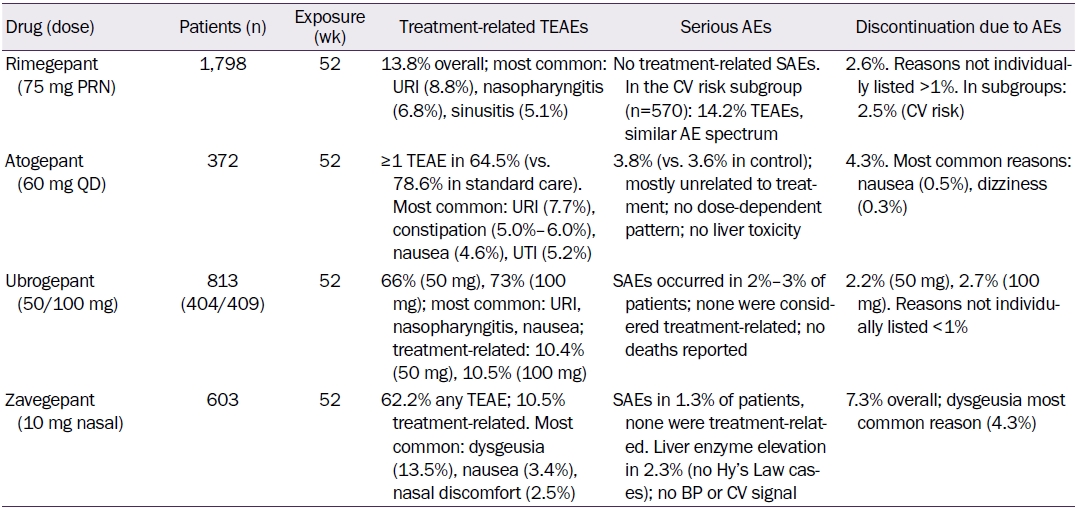
Gepants for Migraine: An Update on Long-Term Outcomes and Safety Profiles |
||
| Soohyun Cho, Kimoon Chang | ||
| DOI: http://doi.org/10.62087/hpr.2025.0012 | ||
|
||
|
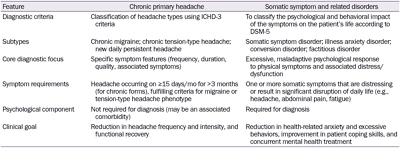
Headache as a Somatic Symptom in Pediatrics: Diagnosis and Integrated Management |
||
| Hye Eun Kwon | ||
| DOI: http://doi.org/10.62087/hpr.2025.0016 | ||
|
||
|
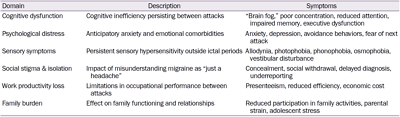
Interictal Burden of Migraine: A Narrative Review |
||
| Soo-Kyoung Kim, Todd J. Schwedt | ||
| DOI: http://doi.org/10.62087/hpr.2025.0018 | ||
|
||
|
The Hidden Risks of Medication Underuse in Migraine Progression |
||
| Heui-Soo Moon, Pil-Wook Chung | ||
| DOI: http://doi.org/10.62087/hpr.2025.0019 | ||
|
||
| Original Article | ||
|
Trigeminal Autonomic Cephalalgias Following Unilateral Dorsolateral Medullary Infarction: A Case Series and Literature Review |
||
| Jae-Myung Kim, Hak-Loh Lee, You-Ri Kang, Joon-Tae Kim, Seung-Han Lee | ||
| DOI: http://doi.org/10.62087/hpr.2025.0013 | ||
|
||
| Case Report | ||
|
Isolated Dental and Lower-Facial Pain Mimicking Trigeminal Neuropathy: An Indirect Carotid-Cavernous Fistula |
||
| Byoungchul Choi, Chulho Kim, Sung-Hwan Kim, Jong-Hee Sohn | ||
| DOI: http://doi.org/10.62087/hpr.2025.0020 | ||
|
||
| Correction | ||
|
Erratum to “Premonitory Symptoms in Migraine: Implications for Disease Burden and Cognitive Impairment, with Some Promising Answers” |
||
| Utku Topbaş, Bahar Taşdelen, Nevra Öksüz Gürlen, Aynur Özge | ||
| DOI: http://doi.org/10.62087/hpr.2024.0031.e1 | ||
|
||
Headache and Pain Research (Headache Pain Res; pISSN: 3022-9057, eISSN: 3022-4764) publishes original articles, review articles, case report, letter to the editor, editorial, and perspective on all aspects of Headache and Pain Research. The main topics include migraine, cluster headache, tension-type headache, intracranial hypotension, intracranial hypertension, reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome, other primary or secondary headache disorders, and issues related headache and pain such as dizziness, psychological, and cognitive problems. Headache and Pain Research is the official journal of Korean Headache Society, and aims to grow into an international journal and welcomes outstanding editorial board members and submissions from all over the world.
It is an Open Access journal, which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. There is no article processing charge. Headache and Pain Research is published 3 times (the last day of February, June, and October) a year.
|
||