Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > Headache Pain Res > Volume 25(1); 2024 > Article
-
Review Article
Update on Cluster Headaches: From Genetic to Novel Therapeutic Approaches -
Myun Kim*
 , Je Kook Yu*
, Je Kook Yu* , Yoo Hwan Kim
, Yoo Hwan Kim
-
Headache and Pain Research 2024;25(1):42-53.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.62087/hpr.2024.0009
Published online: April 22, 2024
Department of Neurology, Hallym University Sacred Heart Hospital, Hallym University College of Medicine, Anyang, Republic of Korea
- Corresponding author: Yoo Hwan Kim, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Neurology, Hallym University Sacred Heart Hospital, Hallym University College of Medicine, 22 Gwanpyeong-ro 170beon-gil, Dongan-gu, Anyang 14068, Republic of Korea Tel: +82-31-380-3740, Fax: +82-31-380-4118, E-mail: drneuroneo@gmail.com
- *These authors contributed equally to this study as co-first authors.
© 2024 The Korean Headache Society
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
- 17,561 Views
- 161 Download
- 10 Crossref
Abstract
- Cluster headaches affect 0.1% of the population and are four times more common in males than in females. Patients with this condition present with severe unilateral head pain localized in the frontotemporal lobe, accompanied by ipsilateral lacrimation, conjunctival injection, nasal congestion, diaphoresis, miosis, and eyelid edema. Recently, the first genome-wide association study of cluster headaches was conducted with the goal of aggregating data for meta-analyses, identifying genetic risk variants, and gaining biological insights. Although little is known about the pathophysiology of cluster headaches, the trigeminovascular and trigeminal autonomic reflexes and hypothalamic pathways are involved. Among anti-calcitonin gene-related peptide monoclonal antibodies, galcanezumab has been reported to be effective in preventing episodic cluster headaches.
INTRODUCTION
CLINICAL FEATURE
EPIDEMIOLOGY
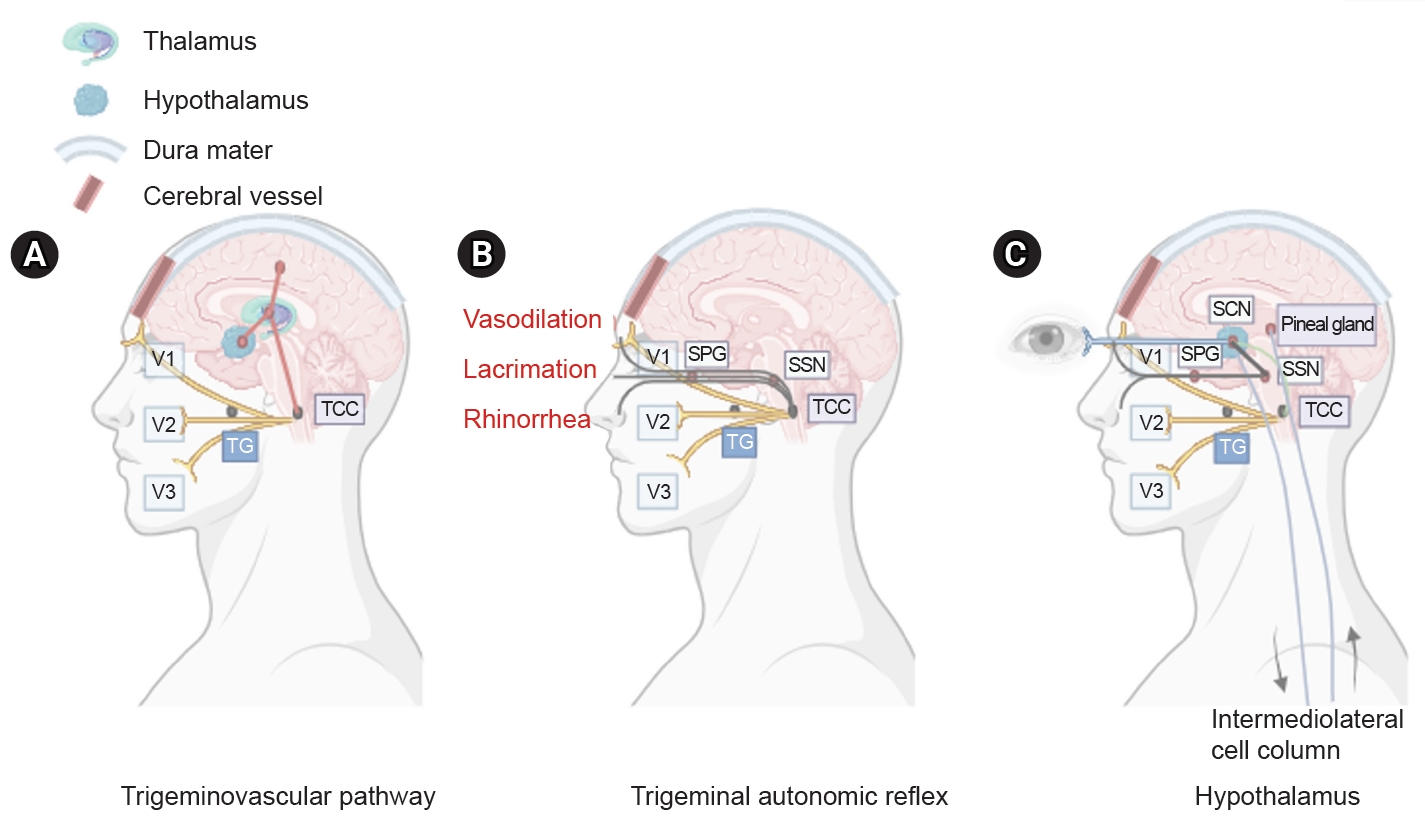
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY
1) Calcitonin gene-related peptide
2) Pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide 38
EVALUATION
MANAGEMENT
1) Oxygen therapy
2) Triptans
1) Corticosteroids
2) Greater occipital nerve injection
1) Verapamil
2) Lithium
3) Topiramate
4) Valproate
5) Gabapentin
6) Melatonin
1) Monoclonal antibodies against calcitonin gene-related peptide
2) Neuromodulation and invasive procedures
3) OnabotulinumtoxinA
SUMMARY
AVAILABILITY OF DATA AND MATERIAL
Not applicable.
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS
Conceptualization: YHK; Data curation: MK, JKY, YHK; Formal analysis: MK, JKY, YHK; Investigation: MK, JKY, YHK; Methodology: YHK; Writing–original draft: MK, JKY; Writing–review and editing: MK, JKY, YHK.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
FUNDING STATEMENT
This research was supported by Hallym University Medical Center Research Fund (YHK).
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
Not applicable.
- 1. Harris W. Neuritis and neuralgia. Lancet 1926;207:885.Article
- 2. Headache Classification Committee of the International Headache Society (IHS). The International Classification of Headache Disorders, 3rd edition. Cephalalgia 2018;38:1-211.ArticlePDF
- 3. Bahra A, May A, Goadsby PJ. Cluster headache: a prospective clinical study with diagnostic implications. Neurology 2002;58:354-361.ArticlePubMed
- 4. May A. Cluster headache: pathogenesis, diagnosis, and management. Lancet 2005;366:843-855.ArticlePubMed
- 5. Drummond PD. Autonomic disturbances in cluster headache. Brain 1988;111:1199-1209.ArticlePubMed
- 6. Drummond PD. Mechanisms of autonomic disturbance in the face during and between attacks of cluster headache. Cephalalgia 2006;26:633-641.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 7. Dodick DW, Rozen TD, Goadsby PJ, Silberstein SD. Cluster headache. Cephalalgia 2000;20:787-803.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 8. Winsvold BS, Harder AVE, Ran C, et al. Cluster headache genomewide association study and meta-analysis identifies eight loci and implicates smoking as causal risk factor. Ann Neurol 2023;94:713-726.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 9. Kudrow L. The cyclic relationship of natural illumination to cluster period frequency. Cephalalgia 1987;7 Suppl 6:76-78.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 10. Russell MB. Epidemiology and genetics of cluster headache. Lancet Neurol 2004;3:279-283.ArticlePubMed
- 11. Kim SA, Choi SY, Youn MS, Pozo-Rosich P, Lee MJ. Epidemiology, burden and clinical spectrum of cluster headache: a global update. Cephalalgia 2023;43:3331024231201577.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 12. Ekbom K, Svensson DA, Träff H, Waldenlind E. Age at onset and sex ratio in cluster headache: observations over three decades. Cephalalgia 2002;22:94-100.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 13. Fourier C, Ran C, Steinberg A, Sjöstrand C, Waldenlind E, Belin AC. Sex differences in clinical features, treatment, and lifestyle factors in patients with cluster headache. Neurology 2023;100:e1207-e1220.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 14. Hoffmann J, May A. Diagnosis, pathophysiology, and management of cluster headache. Lancet Neurol 2018;17:75-83.ArticlePubMed
- 15. Pergolizzi JV Jr, Magnusson P, LeQuang JA, Wollmuth C, Taylor R Jr, Breve F. Exploring the connection between sleep and cluster headache: a narrative review. Pain Ther 2020;9:359-371.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 16. Belin AC, Barloese MC. The genetics and chronobiology of cluster headache. Cephalalgia 2023;43:3331024231208126.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 17. Wei DY, Goadsby PJ. Cluster headache pathophysiology - insights from current and emerging treatments. Nat Rev Neurol 2021;17:308-324.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 18. Zagami AS, Lambert GA. Stimulation of cranial vessels excites nociceptive neurones in several thalamic nuclei of the cat. Exp Brain Res 1990;81:552-566.ArticlePubMed
- 19. Goadsby PJ, Holland PR, Martins-Oliveira M, Hoffmann J, Schankin C, Akerman S. Pathophysiology of migraine: a disorder of sensory processing. Physiol Rev 2017;97:553-622.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 20. O’Connor TP, van der Kooy D. Enrichment of a vasoactive neuropeptide (calcitonin gene related peptide) in the trigeminal sensory projection to the intracranial arteries. J Neurosci 1988;8:2468-2476.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 21. May A, Goadsby PJ. The trigeminovascular system in humans: pathophysiologic implications for primary headache syndromes of the neural influences on the cerebral circulation. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 1999;19:115-127.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 22. Spencer SE, Sawyer WB, Wada H, Platt KB, Loewy AD. CNS projections to the pterygopalatine parasympathetic preganglionic neurons in the rat: a retrograde transneuronal viral cell body labeling study. Brain Res 1990;534:149-169.ArticlePubMed
- 23. Malick A, Strassman RM, Burstein R. Trigeminohypothalamic and reticulohypothalamic tract neurons in the upper cervical spinal cord and caudal medulla of the rat. J Neurophysiol 2000;84:2078-2112.ArticlePubMed
- 24. Ibuka N, Kawamura H. Loss of circadian rhythm in sleep-wakefulness cycle in the rat by suprachiasmatic nucleus lesions. Brain Res 1975;96:76-81.ArticlePubMed
- 25. Chazot G, Claustrat B, Brun J, Jordan D, Sassolas G, Schott B. A chronobiological study of melatonin, cortisol growth hormone and prolactin secretion in cluster headache. Cephalalgia 1984;4:213-220.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 26. Coomans CP, Ramkisoensing A, Meijer JH. The suprachiasmatic nuclei as a seasonal clock. Front Neuroendocrinol 2015;37:29-42.ArticlePubMed
- 27. Edvinsson L, Mulder H, Goadsby PJ, Uddman R. Calcitonin gene-related peptide and nitric oxide in the trigeminal ganglion: cerebral vasodilatation from trigeminal nerve stimulation involves mainly calcitonin gene-related peptide. J Auton Nerv Syst 1998;70:15-22.ArticlePubMed
- 28. Eftekhari S, Edvinsson L. Calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) and its receptor components in human and rat spinal trigeminal nucleus and spinal cord at C1-level. BMC Neurosci 2011;12:112.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 29. Edvinsson L, Haanes KA, Warfvinge K, Krause DN. CGRP as the target of new migraine therapies - successful translation from bench to clinic. Nat Rev Neurol 2018;14:338-350.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 30. McLatchie LM, Fraser NJ, Main MJ, et al. RAMPs regulate the transport and ligand specificity of the calcitonin-receptor-like receptor. Nature 1998;393:333-339.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 31. Russo AF. Calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP): a new target for migraine. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 2015;55:533-552.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 32. Snoer A, Vollesen ALH, Beske RP, et al. Calcitonin-gene related peptide and disease activity in cluster headache. Cephalalgia 2019;39:575-584.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 33. Vollesen ALH, Snoer A, Beske RP, et al. Effect of infusion of calcitonin gene-related peptide on cluster headache attacks: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Neurol 2018;75:1187-1197.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 34. Hannibal J, Ding JM, Chen D, et al. Pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating peptide (PACAP) in the retinohypothalamic tract: a potential daytime regulator of the biological clock. J Neurosci 1997;17:2637-2644.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 35. Tuka B, Szabó N, Tóth E, et al. Release of PACAP-38 in episodic cluster headache patients - an exploratory study. J Headache Pain 2016;17:69.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 36. Lindemann CR. Cluster headache: a review of clinical presentation, evaluation, and management. JAAPA 2022;35:15-19.Article
- 37. Ravishankar K. Classification of trigeminal autonomic cephalalgia: what has changed in International Classification of Headache Disorders-3 beta? Ann Indian Acad Neurol 2018;21:S45-S50.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 38. Headache Classification Subcommittee of the International Headache Society. The International Classification of Headache Disorders: 2nd edition. Cephalalgia 2004;24 Suppl 1:9-160.ArticlePubMed
- 39. Diener HC, May A. Drug treatment of cluster headache. Drugs 2022;82:33-42.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 40. Cohen AS, Burns B, Goadsby PJ. High-flow oxygen for treatment of cluster headache: a randomized trial. JAMA 2009;302:2451-2457.ArticlePubMed
- 41. Oude Nijhuis JC, Haane DY, Koehler PJ. A review of the current and potential oxygen delivery systems and techniques utilized in cluster headache attacks. Cephalalgia 2016;36:970-979.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 42. Bennett MH, French C, Schnabel A, Wasiak J, Kranke P, Weibel S. Normobaric and hyperbaric oxygen therapy for the treatment and prevention of migraine and cluster headache. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2015;2015:CD005219.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 43. Sumatriptan Cluster Headache Study Group. Treatment of acute cluster headache with sumatriptan. N Engl J Med 1991;325:322-326.ArticlePubMed
- 44. Ekbom K, Monstad I, Prusinski A, Cole JA, Pilgrim AJ, Noronha D. Subcutaneous sumatriptan in the acute treatment of cluster headache: a dose comparison study. The Sumatriptan Cluster Headache Study Group. Acta Neurol Scand 1993;88:63-69.ArticlePubMed
- 45. van Vliet JA, Bahra A, Martin V, et al. Intranasal sumatriptan in cluster headache: randomized placebo-controlled double-blind study. Neurology 2003;60:630-633.ArticlePubMed
- 46. Rapoport AM, Mathew NT, Silberstein SD, et al. Zolmitriptan nasal spray in the acute treatment of cluster headache: a double-blind study. Neurology 2007;69:821-826.ArticlePubMed
- 47. Obermann M, Nägel S, Ose C, et al. Safety and efficacy of prednisone versus placebo in short-term prevention of episodic cluster headache: a multicentre, double-blind, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Neurol 2021;20:29-37.ArticlePubMed
- 48. Jammes JL. The treatment of cluster headaches with prednisone. Dis Nerv Syst 1975;36:375-376.PubMed
- 49. Couch JR Jr, Ziegler DK. Prednisone therapy for cluster headache. Headache 1978;18:219-221.ArticlePubMed
- 50. May A, Evers S, Goadsby PJ, et al. European Academy of Neurology guidelines on the treatment of cluster headache. Eur J Neurol 2023;30:2955-2979.ArticlePubMed
- 51. Ambrosini A, Vandenheede M, Rossi P, et al. Suboccipital injection with a mixture of rapid- and long-acting steroids in cluster headache: a double-blind placebo-controlled study. Pain 2005;118:92-96.ArticlePubMed
- 52. Leroux E, Valade D, Taifas I, et al. Suboccipital steroid injections for transitional treatment of patients with more than two cluster headache attacks per day: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Neurol 2011;10:891-897.ArticlePubMed
- 53. Lund NLT, Petersen AS, Fronczek R, et al. Current treatment options for cluster headache: limitations and the unmet need for better and specific treatments: a consensus article. J Headache Pain 2023;24:121.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 54. Leone M, D’Amico D, Frediani F, et al. Verapamil in the prophylaxis of episodic cluster headache: a double-blind study versus placebo. Neurology 2000;54:1382-1385.ArticlePubMed
- 55. Blau JN, Engel HO. Individualizing treatment with verapamil for cluster headache patients. Headache 2004;44:1013-1018.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 56. Cohen AS, Matharu MS, Goadsby PJ. Electrocardiographic abnormalities in patients with cluster headache on verapamil therapy. Neurology 2007;69:668-675.ArticlePubMed
- 57. Damasio H, Lyon L. Lithium carbonate in the treatment of cluster headaches. J Neurol 1980;224:1-8.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 58. Savoldi F, Bono G, Manzoni GC, Micieli G, Lanfranchi M, Nappi G. Lithium salts in cluster headache treatment. Cephalalgia 1983;3 Suppl 1:79-84.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 59. Stochino ME, Deidda A, Asuni C, Cherchi A, Manchia M, Del Zompo M. Evaluation of lithium response in episodic cluster headache: a retrospective case series. Headache 2012;52:1171-1175.ArticlePubMed
- 60. Bussone G, Leone M, Peccarisi C, et al. Double blind comparison of lithium and verapamil in cluster headache prophylaxis. Headache 1990;30:411-417.ArticlePubMed
- 61. Leone M, Dodick D, Rigamonti A, et al. Topiramate in cluster headache prophylaxis: an open trial. Cephalalgia 2003;23:1001-1002.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 62. Mathew NT, Kailasam J, Meadors L. Prophylaxis of migraine, transformed migraine, and cluster headache with topiramate. Headache 2002;42:796-803.ArticlePubMed
- 63. El Amrani M, Massiou H, Bousser MG. A negative trial of sodium valproate in cluster headache: methodological issues. Cephalalgia 2002;22:205-208.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 64. Leandri M, Luzzani M, Cruccu G, Gottlieb A. Drug-resistant cluster headache responding to gabapentin: a pilot study. Cephalalgia 2001;21:744-746.ArticlePubMed
- 65. Leone M, D’Amico D, Moschiano F, Fraschini F, Bussone G. Melatonin versus placebo in the prophylaxis of cluster headache: a double-blind pilot study with parallel groups. Cephalalgia 1996;16:494-496.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 66. Giani L, Proietti Cecchini A, Leone M. Anti-CGRP monoclonal antibodies in cluster headache: what can we learn from recent clinical trials. Neurol Sci 2020;41:485-486.ArticlePDF
- 67. Goadsby PJ, Dodick DW, Leone M, et al. Trial of Galcanezumab in Prevention of Episodic Cluster Headache. N Engl J Med 2019;381:132-141.ArticlePubMed
- 68. Dodick DW, Goadsby PJ, Lucas C, et al. Phase 3 randomized, placebo-controlled study of galcanezumab in patients with chronic cluster headache: results from 3-month double-blind treatment. Cephalalgia 2020;40:935-948.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 69. H. Lundbeck A/S. A 1-year trial to inform about long-term exposure to eptinezumab in participants with chronic cluster headache (cCH) (CHRONICLE) [Internet]. ClinicalTrials.gov; 2023 [cited 2024 Feb 17]. Available from: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT05064397
- 70. Reuter U. Efficacy of erenumab in chronic cluster headache (CHERUB01) [Internet]. ClinicalTrials.gov; 2024 [cited 2024 Feb 17]. Available from: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT04970355
- 71. Gaul C, Magis D, Liebler E, Straube A. Effects of non-invasive vagus nerve stimulation on attack frequency over time and expanded response rates in patients with chronic cluster headache: a post hoc analysis of the randomised, controlled PREVA study. J Headache Pain 2017;18:22.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 72. Magis D, Schoenen J. Advances and challenges in neurostimulation for headaches. Lancet Neurol 2012;11:708-719.ArticlePubMed
- 73. Fontaine D, Lazorthes Y, Mertens P, et al. Safety and efficacy of deep brain stimulation in refractory cluster headache: a randomized placebo-controlled double-blind trial followed by a 1-year open extension. J Headache Pain 2010;11:23-31.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 74. Freund B, Kotchetkov IS, Rao A, et al. The efficacy of botulinum toxin in cluster headache: a systematic review. J Oral Facial Pain Headache 2020;34:129-134.ArticlePubMed
- 75. Lampl C, Rudolph M, Bräutigam E. OnabotulinumtoxinA in the treatment of refractory chronic cluster headache. J Headache Pain 2018;19:45.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 76. Bratbak DF, Nordgård S, Stovner LJ, et al. Pilot study of sphenopalatine injection of onabotulinumtoxinA for the treatment of intractable chronic cluster headache. Cephalalgia 2016;36:503-509.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 77. Sostak P, Krause P, Förderreuther S, Reinisch V, Straube A. Botulinum toxin type-A therapy in cluster headache: an open study. J Headache Pain 2007;8:236-241.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
REFERENCES
Figure & Data
References
Citations

- Exercise as an abortive treatment for cluster headaches: Insights from a large patient registry
Mi‐Kyoung Kang, Yooha Hong, Soo‐Jin Cho
Annals of Clinical and Translational Neurology.2025; 12(1): 149. CrossRef - Morning Headaches: An In-depth Review of Causes, Associated Disorders, and Management Strategies
Yooha Hong, Mi-Kyoung Kang, Min Seung Kim, Heejung Mo, Rebecca C. Cox, Hee-Jin Im
Headache and Pain Research.2025; 26(1): 66. CrossRef - Does Laterality Matter? Insights Into Unilateral Pain in Cluster Headache
Tae-Jin Song
Journal of Clinical Neurology.2025; 21(3): 157. CrossRef - Pain Lateralization in Cluster Headache and Associated Clinical Factors
Soohyun Cho, Mi Ji Lee, Min Kyung Chu, Jeong Wook Park, Heui-Soo Moon, Pil-Wook Chung, Jong-Hee Sohn, Byung-Su Kim, Daeyoung Kim, Kyungmi Oh, Byung-Kun Kim, Soo-Jin Cho
Journal of Clinical Neurology.2025; 21(3): 220. CrossRef - Subtype shift, relapse rate and risk factors of frequent relapse in cluster headache: A multicenter, prospective, longitudinal observation
Mi Ji Lee, Soo-Kyoung Kim, Min Kyung Chu, Jae Myun Chung, Heui-Soo Moon, Pil-Wook Chung, Jeong Wook Park, Byung-Kun Kim, Kyungmi Oh, Yun-Ju Choi, Jong-Hee Sohn, Byung-Su Kim, Dae Woong Bae, Daeyoung Kim, Tae-Jin Song, Kwang-Yeol Park, Soo-Jin Cho
Cephalalgia.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Inverse association of obesity with bout periodicity in episodic cluster headache: a multicenter cross-sectional study
Byung-Su Kim, Mi Ji Lee, Byung-Kun Kim, Jong-Hee Sohn, Tae-Jin Song, Min Kyung Chu, Soo-Kyoung Kim, Jeong Wook Park, Heui-Soo Moon, Pil-Wook Chung, Soo-Jin Cho
The Journal of Headache and Pain.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Trigeminal Autonomic Cephalalgias Following Unilateral Dorsolateral Medullary Infarction: A Case Series and Literature Review
Jae-Myung Kim, Hak-Loh Lee, You-Ri Kang, Joon-Tae Kim, Seung-Han Lee
Headache and Pain Research.2025; 26(3): 218. CrossRef - Isolated Dental and Lower-Facial Pain Mimicking Trigeminal Neuropathy: An Indirect Carotid-Cavernous Fistula
Byoungchul Choi, Chulho Kim, Sung-Hwan Kim, Jong-Hee Sohn
Headache and Pain Research.2025; 26(3): 226. CrossRef - Side Shift of Attacks in Cluster Headache: A Prospective Single-center Study
Michelle Sojung Youn, Jun Pyo Kim, Mi Ji Lee
Headache and Pain Research.2024; 25(2): 96. CrossRef - Reduction of neck pain severity in patients with medication-overuse headache
Yooha Hong, Hong-Kyun Park, Mi-Kyoung Kang, Sun-Young Oh, Jin-Ju Kang, Heui-Soo Moon, Tae-Jin Song, Mi Ji Lee, Min Kyung Chu, Soo-Jin Cho
The Journal of Headache and Pain.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
 PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link-
 Cite this Article
Cite this Article
- Cite this Article
-
- Close
- Download Citation
- Close
- Figure
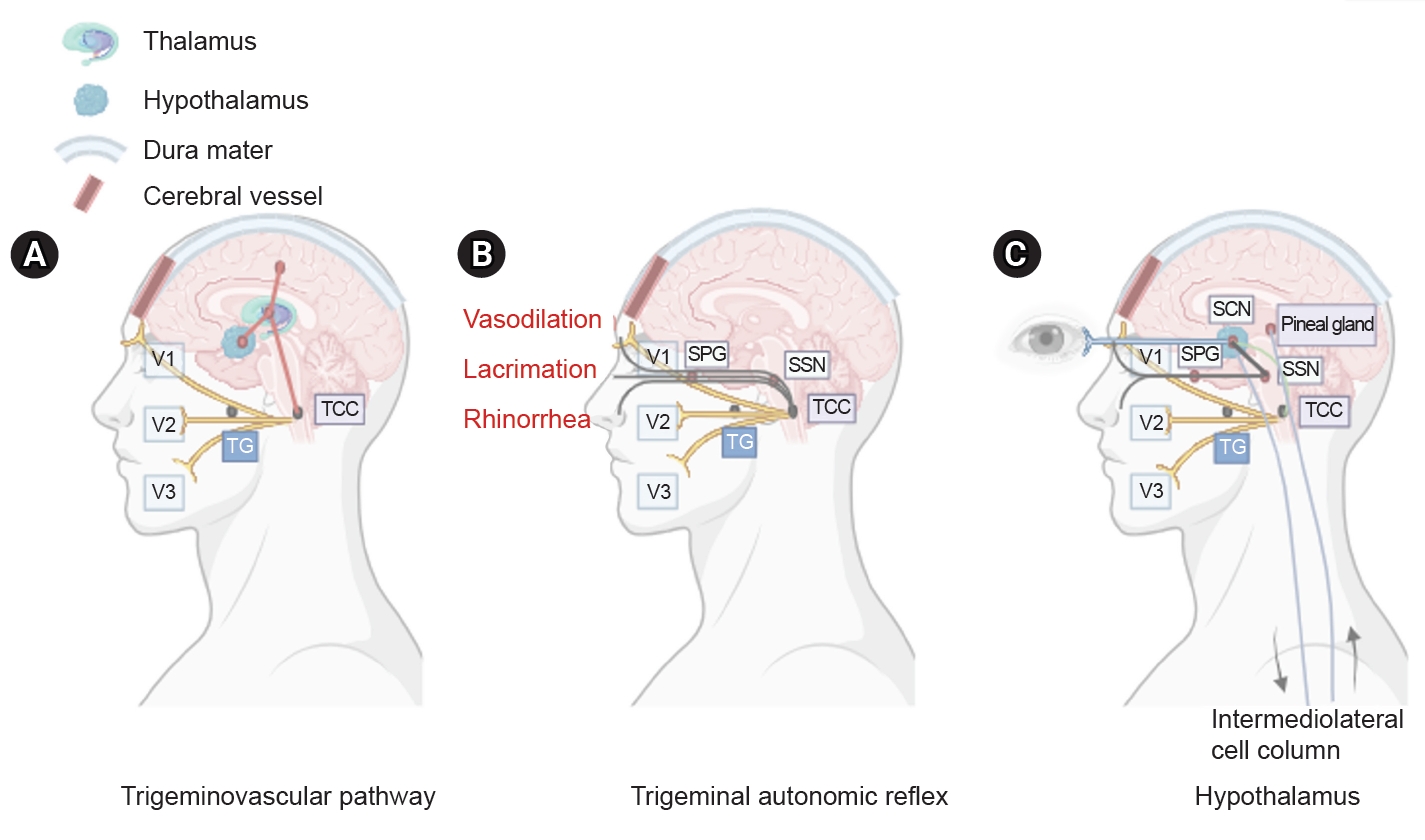
Figure 1.
| Diagnostic criteria of cluster headache (ICHD-2) | Diagnostic criteria of cluster headache (ICHD-3) |
| A. At least five attacks fulfilling criteria B–D | A. At least five attacks fulfilling criteria B–D |
| B. Severe or very severe unilateral orbital, supraorbital and/or temporal pain lasting 15–180 minutes if untreated | B. Severe or very severe unilateral orbital, supraorbital and/or temporal pain lasting 15–180 minutes (when untreated) |
| C. Headache is accompanied by at least one of the following: | C. Either or both of the following: |
| 1. Ipsilateral conjunctival injection and/or lacrimation | 1. at least one of the following symptoms or signs, ipsilateral to the headache: |
| 2. Ipsilateral nasal congestion and/or rhinorrhea | a) conjunctival injection and/or lacrimation |
| 3. Ipsilateral eyelid edema | b) nasal congestion and/or rhinorrhea |
| 4. Ipsilateral forehead and facial sweating | c) eyelid edema |
| 5. Ipsilateral miosis and/or ptosis | d) forehead and facial sweating |
| 6. A sense of restlessness or agitation | e) miosis and/or ptosis |
| D. Attacks have a frequency from one every other day to 8 per day | 2. a sense of restlessness or agitation |
| E. Not attributed to another disorder | D. Occurring with a frequency between one every other day and eight per day |
| E. Not better accounted for by another ICHD-3 diagnosis. |
| Treatment | Dose | Evidence | Adverse events |
|---|---|---|---|
| Treatment of acute cluster attacks | |||
| Oxygen | 12 L/min, 100% | +++ | - |
| Sumatriptan s.c. | 6 mg | +++ | Feeling of pressure, warmth, heaviness, chest pain, local reaction at the injection site, drowsiness, feeling of weakness, increase or decrease in blood pressure, bradycardia, tachycardia |
| Sumatriptan nasal spray | 20 mg | ++ | |
| Zolmitriptan nasal spray | 5 mg | ++ | |
| Bridging therapy for cluster headaches | |||
| Prednisone | 100 mg tapering by 20 mg every 2–3 days | ++ | Depression, irritability, euphoria, stomach problems, GI ulcer, blood glucose increase, sleep disorders |
| Greater occipital nerve block | ++ | Local irritation | |
| Preventive therapy for cluster headaches | |||
| Verapamil | 200–960 mg | ++ | Hypotension, fatigue, constipation, edema, bradycardia, AV block |
| Lithium | ++ | Tremor, acne, goiter, hypothyroidism, muscle weakness | |
| Topiramate | 100–150 mg | + | Cognitive dysfunction, fatigue, dizziness, paresthesia, mood swings, anxiety, weight loss, hair loss |
| Gabapentin | 1,000–1,800 mg | (+) | Dizziness, somnolence, peripheral edema |
| Melatonin | 10 mg | (+) | Daytime sleepiness, headache dizziness, hypothermia |
| Galcanezumab | 120 mg s.c. once monthly | + | Local reaction, hypersensitivity, constipation |
ICHD, International Classification of Headache Disorder.
s.c., subcutaneous; GI, gastrointestinal; AV, atrioventricular; +++, a high level of evidence from studies; ++, moderate evidence from studies; +, low evidence; (+), questionable evidence.
Table 1.
Table 2.
TOP
 KHS
KHS




