Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > Headache Pain Res > Volume 25(1); 2024 > Article
-
Review Article
Menstrual Migraine: A Review of Current Research and Clinical Challenges -
Jong-Geun Seo

-
Headache and Pain Research 2024;25(1):16-23.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.62087/hpr.2024.0004
Published online: April 22, 2024
Department of Neurology, Kyungpook National University School of Medicine, Daegu, Republic of Korea
- Correspondence: Jong-Geun Seo, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Neurology, Kyungpook National University Hospital, Kyungpook National University School of Medicine, 130 Dongdeok-ro, Jung-gu, Daegu 41944, Republic of Korea Tel : +82-53-200-5765, Fax : +82-53-422-4265, E-mail: jonggeun.seo@gmail.com
© 2024 The Korean Headache Society
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
- 24,698 Views
- 290 Download
- 6 Crossref
Figure & Data
References
Citations

- Sex hormones and diseases of the nervous system
Hyman M. Schipper
Brain Medicine.2025; : 1. CrossRef - Evidence-Based Recommendations on Pharmacologic Treatment for Migraine Prevention: A Clinical Practice Guideline from the Korean Headache Society
Byung-Su Kim, Pil-Wook Chung, Jae Myun Chung, Kwang-Yeol Park, Heui-Soo Moon, Hong-Kyun Park, Dae-Woong Bae, Jong-Geun Seo, Jong-Hee Sohn, Tae-Jin Song, Seung-Han Lee, Kyungmi Oh, Mi Ji Lee, Myoung-Jin Cha, Yun-Ju Choi, Miyoung Choi
Headache and Pain Research.2025; 26(1): 5. CrossRef - Morning Headaches: An In-depth Review of Causes, Associated Disorders, and Management Strategies
Yooha Hong, Mi-Kyoung Kang, Min Seung Kim, Heejung Mo, Rebecca C. Cox, Hee-Jin Im
Headache and Pain Research.2025; 26(1): 66. CrossRef - Migraine in Women: Inescapable Femaleness?
Soo-Kyoung Kim
Headache and Pain Research.2024; 25(1): 1. CrossRef - Three-month treatment outcome of medication-overuse headache according to classes of overused medications, use of acute medications, and preventive treatments
Sun-Young Oh, Jin-Ju Kang, Hong-Kyun Park, Soo-Jin Cho, Yooha Hong, Mi-Kyoung Kang, Heui-Soo Moon, Mi Ji Lee, Tae-Jin Song, Young Ju Suh, Min Kyung Chu
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Understanding the Connection between the Glymphatic System and Migraine: A Systematic Review
Myoung-Jin Cha, Kyung Wook Kang, Jung-won Shin, Hosung Kim, Jiyoung Kim
Headache and Pain Research.2024; 25(2): 86. CrossRef
 PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link-
 Cite this Article
Cite this Article
- Cite this Article
-
- Close
- Download Citation
- Close
- Figure
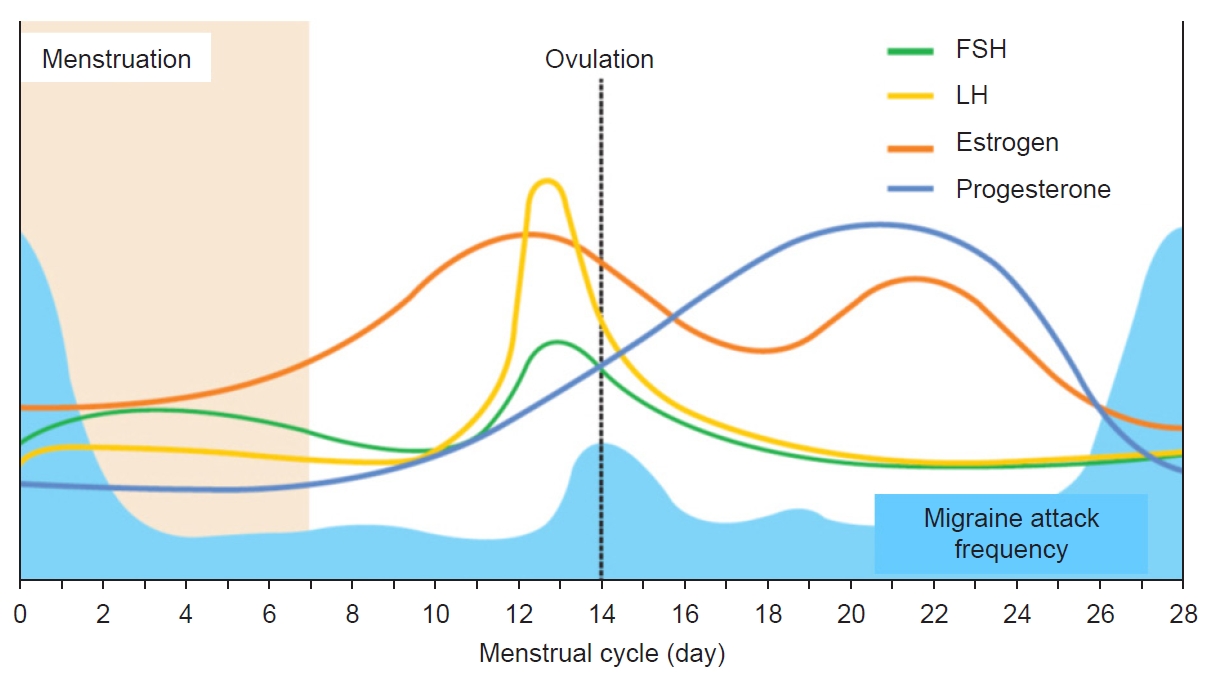
Figure 1.
| Pure menstrual migraine |
| A. Attacks, in a menstruating woman*, fulfilling criteria for migraine without/with aura and criterion B below. |
| B. Occurring exclusively on day 1±2 (i.e., days −2 to +3)† of menstruation in at least two out of three menstrual cycles and at no other times of the cycle. |
| Menstrually-related migraine |
| A. Attacks, in a menstruating woman*, fulfilling criteria for migraine without/with aura and criterion B below. |
| B. Occurring on day 1±2 (i.e., days −2 to +3)† of menstruation in at least two out of three menstrual cycles, and additionally at other times of the cycle. |
| Acute treatment | Short-term prevention |
|---|---|
| NSAIDs49 | NSAIDs65 |
| Ergotamine derivatives21 | |
| Triptans | Triptans |
| Frovatriptan52 | Frovatriptan63 |
| Naratriptan45 | Naratriptan22,23 |
| Sumatriptan48 | Sumatriptan24 |
| Zolmitriptan50 | Zolmitriptan64 |
| Almotriptan44 | |
| Rizatriptan46 |
*For the purposes of ICHD-3, menstruation is considered to be endometrial bleeding resulting either from the normal menstrual cycle or from the withdrawal of exogenous progestogens, as in the use of combined oral contraceptives or cyclical hormone replacement therapy. †The first day of menstruation is day 1 and the preceding day is day −1; there is no day 0.
NSAIDs, nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs.
Table 1.
Table 2.
TOP
 KHS
KHS